
|
九韶内核 1.0.0.0
|

|
九韶内核 1.0.0.0
|
边界表达(Boundary Representation,简称BRep)是当前最流行的数据结构。BRep可以在减轻存储压力的同时,保持完备性和无歧义。BRep使用实体边界上的点、线、面来表示实体,实体的体信息由包含在边界内的三维空间导出。其两个基本元素为:几何信息(Point、Curve、Surface);拓扑信息(Vertex、Edge、Face连接关系)。
我们先给出一个BRep结构的各级拓扑结构的定义:

接下来我们将举一些例子,方便您更好的理解。
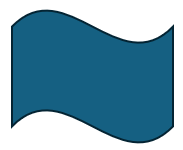
不难看出,这个例子有 4 个 Vertex,4 个 Edge,1 个 Wire,1 个 Face。
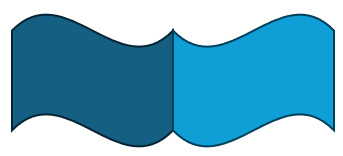
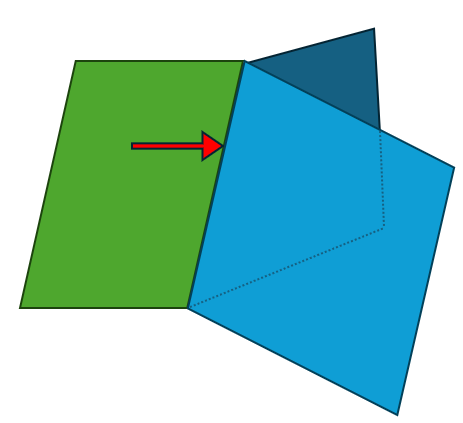
因为中间重合部分的 Vertex 和 Edge 是共用的,所以这个例子有 6 个 Vertex,7 个 Edge,2 个 Wire,2 个 Face,1 个 Shell。
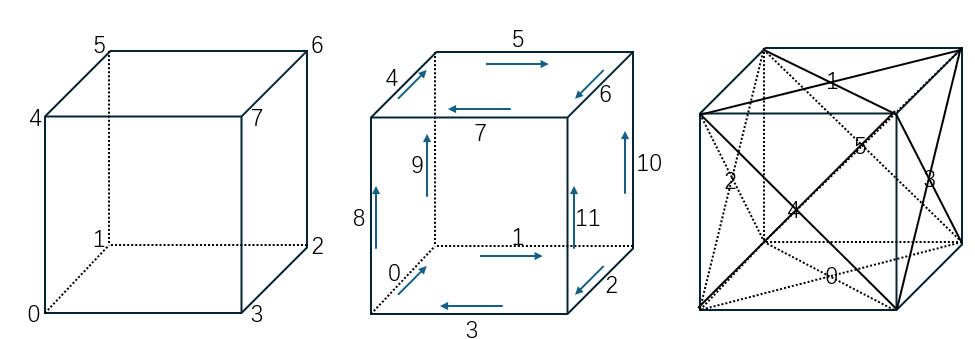
这个例子有 8 个 Vertex,12 个 Edge,6 个 Wire,6 个 Face,1 个 Shell。

这个例子有 2 个 Vertex,3 个 Edge,3 个 Wire,3 个 Face,1 个 Shell。而 0 号 Edge 在 Wire 中被复用了,所以这是一条经典的 Seam Edge。
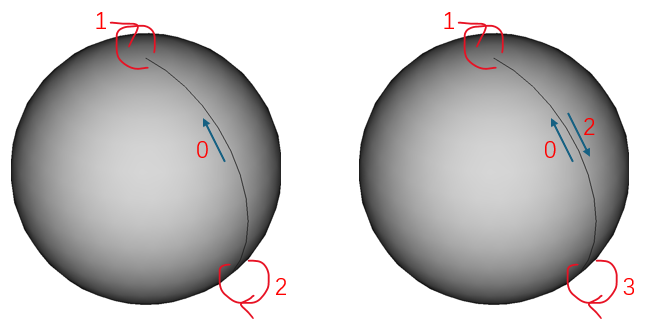 |  |
这个例子有 2 个 Vertex,3 个 Edge,1 个 Wire,1 个 Face,1 个 Shell。在这个例子中不仅有 Seam Edge,还有两条没有长度的Edge。事实上,这两条 Edge 尽管在 3D 中没有长度,但是在参数域上是有长度的,所以这是两条经典的 Degenerated Edge(退化边)。
接下来,我们将介绍比较常见的几种 Edge。
在一个封闭的 TopoShape(这里指 Shell、Solid)内,通常来说最常见的 Edge 是两个不同 Face 的邻接 Edge。普通 Edge 属于两个不同的 Face,且长度不为 0。

一个常见的特例是圆柱的侧边,这条 Edge 被一个 Face 所有,且在 Face 的一个 Wire 中出现两次(一次正,一次反)。Seam Edge 是合法的。

一个常见的特例是球的顶边,这条 Edge 长度为 0,退化成了一个点。退化 Edge 是合法的。

只属于 1 个 Face,且在 Face 的 1 个 Wire 中只出现一次的 Edge 称为自由 Edge。自由 Edge 在封闭 TopoShape 中是非法的。

在 1 个 Shape 或 Solid 中,属于超过 2 个 Face 的 Edge 称为非流形 Edge。非流形 Edge 是非法的。
首先我们先来介绍一下 TopoShape 的树状结构,如下图所示:
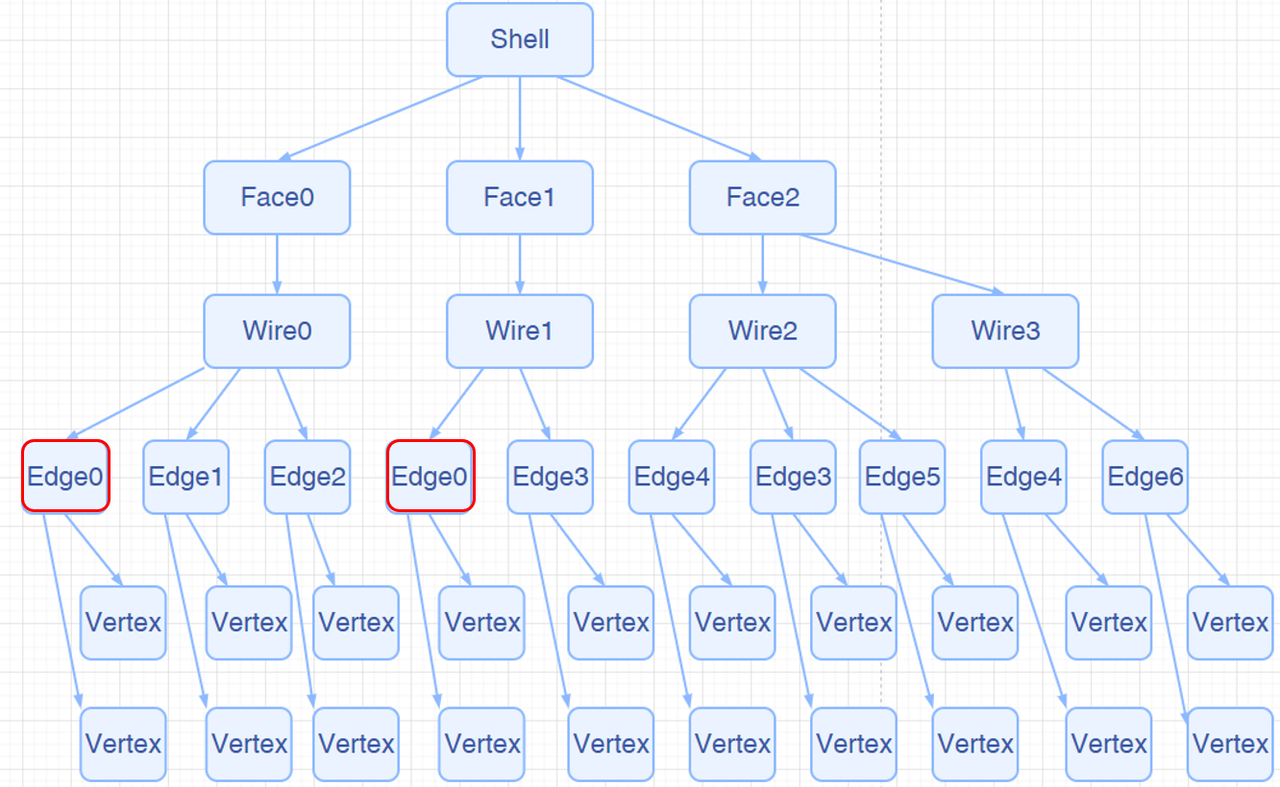
对一个拓扑结构进行遍历是十分常见的操作,我们内核提供两种方式: AMCAX::TopoExplorer 和 AMCAX::WireExplorer ,接下来我们将对这两种方式进行逐一介绍。
AMCAX::TopoExplorer 可以实现对 TopoShape 中的指定类型( Shape , Compound , CompSolid , Solid , Shell , Face , Wire , Edge , Vertex)按照树状结构进行先序遍历,找到指定类型的子 shape。比如,遍历一个 TopoShape 的面可以用如下代码:
需要注意的是, AMCAX::TopoExplorer 不会考虑重复性(IsSame级别的“相等”),也就是说,如果一条 Edge 被两个 Face 共用,那 AMCAX::TopoExplorer 仍然会遍历这条 Edge 两次。如果不希望遍历两次,则可以使用一个 std::unordered_set 来去重,代码如下:
在上文中,我们提到了重复性,重复性其实隐含了“相等”的定义。接下来我们将介绍关于 TopoShape 三种层次的“相等”,严格程度逐渐增加:

不难发现,当我们需要对某一个 Wire 的 Edge 按顺序遍历时, AMCAX::TopoExplorer 其实是不能满足需求的。这时, AMCAX::WireExplorer 可以满足这样的需求,不过遍历速度会变慢。
由于树状结构和先序遍历的存在,事实上每条 Edge(其他的 Vertex、Wire、Face 也是类似的)都有自己的序号。而 AMCAX::TopoExplorerTool 类提供了一些快捷的遍历操作, AMCAX::TopoExplorerTool::MapShapes 可以获得某类拓扑结构的有序号集合(如 Edge),并且得到的集合是去重的。
事实上,这个序号和在 FreeCAD 中左下角显示的序号是一致的(FreeCAD 从 1 开始,而我们内核从 0 开始)。
AMCAX::TopoExplorerTool::MapShapesAndAncestors 可以获取子 shape 到所属的父 shape 的 Map,而 AMCAX::TopoExplorerTool::MapShapesAndUniqueAncestors 同样可以获取 Map,两者的区别在于当输入 seam 边时,MapShapesAndUniqueAncestors 会返回 1 个所属 face,而 MapShapesAndAncestors 会返回 2 个所属 face。比如 Edge 到所属 Face 的 Map 可以这样获得:
判断一条 Edge 是否是退化的是非常重要的,比如我们不应当在一条退化边上进行采样。我们可以通过 AMCAX::TopoTool::Degenerated 来判断。
可以通过 AMCAX::TopoTool::IsClosed 来判断一条 Edge 是否为 Seam 边。
Vertex 中只有一个 Point,表示三维空间中的点。而从 Vertex 中获取 Point 的方法为 AMCAX::TopoTool::Point :
curve3d 是 3 维参数曲线。pcurve是 2 维参数曲线。pcurve 是与 <Edge, Surface, Location> 绑定的,即 Edge, Surface, Location 是一条 pcurve 的索引。
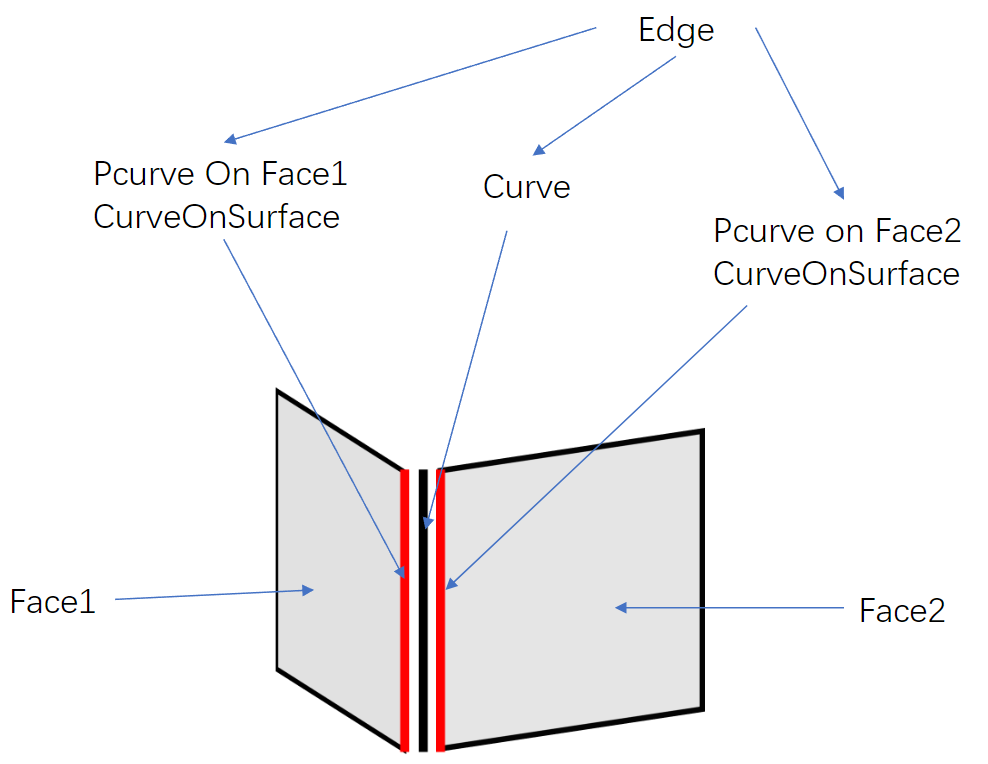
一个 Edge 中通常有一条 curve3d,两条 pcurve。事实上,通过 pcurve 和 surface 还可以构建一条 3 维参数曲线,但由于 Tolerance 的存在,所以创建出来的两条 3 维参数曲线与 curve3d 基本不会重合。在几何建模的过程中,Edge 中的 Curve 数量没有要求,没有 Curve 也没有问题。但除特殊情况外,最终的几何模型应当包含 1 条 curve3d 和 2 条 pcurve。
接下来我们将介绍几种特殊情况:
如果 Edge 位于一个平面(Geom3Plane)上,则不需要额外的 pcurve。因为平面上的 Edge 可以直接通过 Curve3d 来表示。
Seam Edge 有 1 条 curve3d 和两条 pcurve,这两条 pcurve 都在 1 个 Face 上,两条 pcurve 的区别在于 Edge 的 Orientation:一条 pcurve 对应 Edge 的正向,另一条 pcurve 对应 Edge 的反向。
Degenerated Edge 只有 1 条 pcurve,没有 curve3d。
自由 Edge 有 1 条 curve3d,1 条 pcurve。
需要注意的是,内核不提供为 curve3d 计算 pcurve 的功能。正确的建模方式应当是先构建 pcurve,然后用 pcurve 和 surface 计算 curve3d:
获取 Edge 的 Curve3d 的方法是 AMCAX::TopoTool::Curve 。
有几点需要注意:
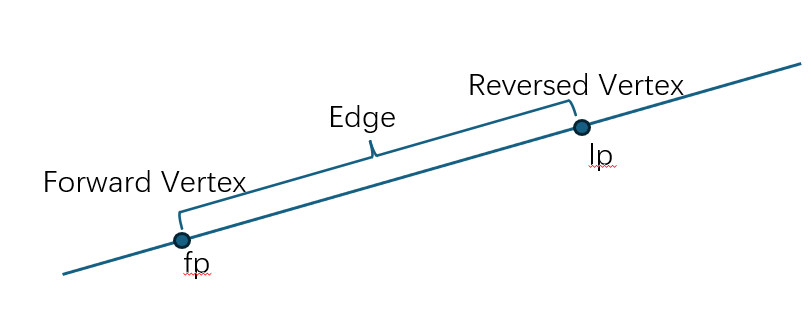
1.接口返回的是原始的曲线,或者说,如果一条 Edge 是一个 Geom3Line 和两个 Vertex 构成的线段,那么这个接口获取到的是一条无限长的直线(Geom3Line),fp 和 lp 是两个 Vertex 在曲线上的参数。
2.AMCAX::TopoTool::Curve 有重载函数,一个输入 loc 而另一个没有。输入 loc 的接口得到的一定是指向 edge 中曲线内存的一个指针,而没输入 loc 的接口,在 edge 的 location 为空时,返回指向内存的指针,非空时返回指向一条新构建曲线的指针。
3.如果输入的是一个退化边,会返回空指针。
4.输入 loc 的接口获得的 Curve 和实际的位置差了一个 location,而对 Curve 直接应用 location.Transformation() 是禁止的,这会改变 edge 的内容。正确的做法是,复制一份 Curve 再对 CopyCurve 进行变换:
获取 pcurve 的方法是 AMCAX::TopoTool::CurveOnSurface 。
需要注意的是,如果输入的是 seam 边,需要特殊处理,根据 Edge 的 Orientation 会返回不同的 pcurve:
在上面的示例中,获取了圆柱 seam 边的两条 pcurve ,这两条 pcurve 的朝向始终一致,与 curve3d 的朝向一致,这不需要考虑 edge 的朝向。
一个 Face 中只有一个 Surface。获取 Surface 的方式是 AMCAX::TopoTool::Surface 。
输入 loc 的接口获得的 Surface 和实际的位置差了一个 location,而对 Surface 直接应用 location.Transformation() 是禁止的,这会改变 face 的内容。正确的做法是,复制一份 Surface 再对 CopySurface 进行变换:
Mesh 指的是三角网格。Mesh 在 CAD 中的存在意义是渲染。由于 OpenGL 的绘制基本单元是点、线段、三角形,因此曲线必须离散成多边形进行绘制,曲面必须离散成 Mesh 进行绘制,因此在包含图形用户界面(GUI)的应用程序中,看到的 BRep 模型通常是通过三角网格来可视化的。如下图所示。
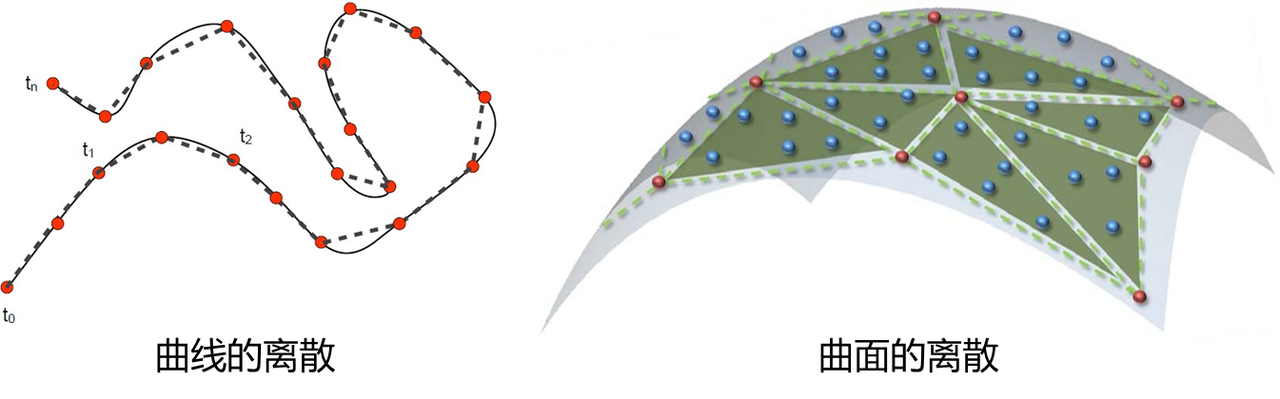
显然,离散会带来误差,这意味着在包含 GUI 的应用程序中显示的 BRep 模型并不是模型本身,而是模型的 Mesh,二者之间的误差由离散精度,即网格的疏密程度决定,考虑到 CAD 模型的 Mesh 生成必须非常快,Mesh 的精度可想而知并不高。

由离散带来的问题是非常多的,如通过视觉判断两个事实上相同的圆是否重叠,或两个相同的球是否重叠,就会出现下图所示的情况。或者将光滑曲面渲染成出现褶皱的情况。另一类问题是网格生成失败,这会导致存在破洞。因此看到模型上有洞,需要综合考量 Mesh 的原因和模型本身的原因。

接下来我们将介绍 Mesh 的生成、获取、读写方法。
虽然 Mesh 对于渲染而言是必要的,但不一定要在模型构建后使用内核为模型生成 Mesh ,因为包含 GUI 的软件会自行生成 Mesh,进而用于渲染。渲染中的法向是一个关键信息,如果 Mesh 不提供法向,渲染时会根据 Mesh 自动计算一个近似的法向。如果需要确保三角网格的法向和 CAD 模型的法向是一致的,则可以使用 AMCAX::MakeShapeTool::EnsureNormalConsistency() 。
快捷创建拓扑结构是一个基础需求,而 AMCAX::MakeVertex 、 AMCAX::MakeEdge 、 AMCAX::MakeWire 、 AMCAX::MakeFace 等提供了不同拓扑结构的快捷创建方式,这是非常常用也是非常重要的功能。
创建 Vertex 可以通过一个 Point3 来创建:
AMCAX::MakeEdge 可以根据 Curve 快捷创建 Edge。如果 MakeEdge 的输入中没有 Vertex,那么 MakeEdge 会自动构建两个 Vertex。这意味着,如果想要用 MakeEdge 构建两条相连的 Edge,务必注意 Vertex 的共用问题,简单地构建只会得到 2 个 Edge 和 4 个 Vertex。此外,退化边也是可以用 MakeEdge 构建的。MakeEdge 功能众多,我们将分类介绍:
可以通过两个 Point3 构建线段 Edge,也可以用两个 TopoVertex 构建。需要注意的是两个 Point3/TopoVertex 的距离要大于 AMCAX::Precision::Confusion(),否则就会被判断为同一个 Point3/TopoVertex。
比如可以基于 Circle3,Line3 等数学表达构建,以下以 Line3 为例:
另外 MakeEdge 会根据数学表达自动调整参数、Point3、Vertex 的顺序,以及 Vertex 的 Orientation:
这是从 curve 构建 Edge 的重要功能。在这里 MakeEdge 仍然会自动调整参数、Point3、Vertex 的顺序,以及 Vertex 的 Orientation。构建方法如下:
需要注意的是基于 pcurve 和 Surface 构建的 Edge 是没有 curve3d 的。构建方法如下:
构建一个wire可以通过以下两种方式:
注:每次添加的边必须与之前已经添加的 edge 在几何上是相连的。如上面的例子,如果按照e1—e3—e2—e4的顺序进行添加,那么在添加 e3 的时候会因为不与 e1 相连导致添加不了,此时调用 IsDone() 会返回 false,调用 Error() 会返回 WireError::DisconnectedWire。如果能确定需要连成 wire 的 edge 是相连的,但不知道相连关系,那么必须使用下面一次性添加 edge list 的方式。
列表中 edge 的顺序不会影响构造的结果。
注:MakeWire 能够构建不包含 Seam Edge、退化边的 Wire,支持单独添加 Edge 或添加 Edge的 list。MakeWire 不能正确构建含有退化边的wire,因为此接口会根据顶点 3D 点的几何位置来判断定向,而退化边的顶点是同一个,因此添加的退化边的定向可能不正确。MakeWire 不能正确构建含有非流形顶点的 wire,此接口要求在一个 wire 内的顶点的度数必须为2(或1,即开的 wire 端点)。
AMCAX::MakeFace 功能也很多,我们将分类进行介绍:
可以基于 Plane,Cylinder 等数学表达构建:
基于 Geom3Surface 的 Face 构建是 MakeFace 最常用的功能:
MakeFace 要求在提供 Surface 的同时提供 Tolerance。需要注意的是,当输入的曲面为无穷大,且没有约束参数范围时,不会自动生成 Wire。其余情况都会自动生成 wire。
当 Wire 是平面上的 Wire 时,单独输入 Wire 构建 Face 是可以构建成功的:
注:输入不在平面上的 Wire 可能会构建失败。
注:需要提供 Face 表示的区域在 Wire 的内部还是外部(最后的 bool 参数,true 表示在内部)。
将 Wire 添加到 Face 中:
执行后,结果如下图所示:左边为 face7,右图为 face8。

但是要注意 Wire 的 Orientation,也就是说,如果这样写,便会得到错误的结果:
而修正的方式是在 Edge 或 Wire 层级将其 Orientation 设为 Reversed:
尽管 Make*.hpp 提供了一些方便的构建 TopoShape 的 API,但是部分建模问题只有 TopoBuilder 能够解决。接下来我们将介绍 TopoBuilder 构建不同拓扑结构的方法。
AMCAX::TopoBuilder::MakeVertex 提供构建一个顶点的功能。
针对不同类型的 Edge 有不同的构建方法。我们将逐一介绍:
正常的建模思路是,通过几何计算得到了全部所需的 Point、Curve3d 和 PCurve,再构建拓扑结构:
第一步:准备好 Curve3d,根据 curve 构建 Edge。
AMCAX::TopoBuilder::Range 设置了 TopoEdge 的参数范围,如果 curve 的参数范围与 edge 期待的参数范围一致时,这一步可以省略。
第二步:准备起始 Vertex 和终止 Vertex,为 Edge 添加 Vertex。
注:在这里要注意起始 Vertex 和终止 Vertex 的 Orientation。Edge 的起始 Vertex 是 Forward,终止 Vertex 是 Reversed。 Orientation 默认是 Forward ,所以需要对终止 Vertex 的 Orientation 进行改变。改变有两种形式:一是对自身进行改变,二是不对自身进行改变,产生一个新的。其中 AMCAX::TopoShape::SetOrientation 和 AMCAX::TopoShape::Reverse 对自身进行改变, AMCAX::TopoShape::Oriented 不对自身进行改变,而是产生一个新的,然后传入到 builder 里。
第三步:在构建好 Face 后,添加 pcurve:
要注意 pcurve 的方向应该与 curve3d 保持一致,edge 的 Orientation 对 pcurve 的方向没有任何影响,记住“几何是几何,拓扑是拓扑”。 而添加 Vertex 的步骤只要在 MakeEdge 后就可以,也就是说第二步第三步互换是没有问题的,在 Range 前添加 Vertex 也是没有问题的。
其他的步骤都相同,仅第三步有所不同:
要注意 pcurve1、pcurve2 的方向仍然应该与 curve3d 保持一致。两个 pcurve 的区别是:pcurve1 是 Forward edge 在 Surface 参数域上的 pcurve,pcurve2 是 Reversed edge 在 Surface 参数域上的 pcurve。
其他的步骤都相同,仅第一步不同,没有 curve3d:
在这里要注意将退化 Flag 设为 True。而 pcurve 的方向无需考虑与 curve3d 保持一致,只需与 edge 的 Orientation 保持一致即可。
其他的步骤都相同,仅第三步不同,只有 1 条 pcurve。
正常的思路是:
第一步先根据参数域上的 Wire 确定 Wire 的方向,再确定好选用哪些 Edge,这些 Edge 的 Orientation是什么:
第二步构建并向 Wire 添加 Edge:
这里的 Edge 的添加顺序可以是任意的。
第三步将 Wire 的 Closed Flag 设置好:
构建 Face 的方法如下:
构建 Shell 时需要注意 Closed Flag,方法如下:
构建 Solid 的方式如下:
构建 Compound 的方式如下:
OrientationType 共有 4 种类型:Forward,Reversed,Internal,External,其中最常用的是 Forward 和 Reversed。任何一级的 TopoShape 都可以用 SetOrientation() 来设置 Orientation,或者用 Orientation() 来获取 Orientation。如果想获得一个与当前 TopoShape 只有 Orientation 不同的 TopoShape,可以使用 Orientated() 。Orientation 是与几何、Location 独立的成员,改变任何一个不会影响其他任意成员。
对于一条 Edge ,其起始 Vertex 的 Orientation 为 Forward,终止 Vertex 的 Orientation 为 Reversed。比如一个线段 Edge 有两个不同的 Vertex,则 Orientation 一个是 Forward,另一个是 Reversed。再比如圆构成的 Edge 有两个相同的 Vertex,但 Orientation 也是一个为 Forward,另一个为 Reversed。
注:在上面这个例子中,因为圆构成的 Edge 有两个相同的 Vertex,所有只需要构造一个顶点就可以,这时 AMCAX::TopoTool::IsClosed(edge) 会返回 true。如果构造了两个顶点,那么 AMCAX::TopoTool::IsClosed(edge) 会返回 false。
Edge 的 Forward 方向是 curve3d 的方向。如果没有 curve3d 就是 pcurve 的方向。Reversed Edge 的方向与 curve 方向相反。
比如已知三条用 xoy 平面上的 3d curve 构建的 Edge,以及用自然标架构造的 Geom3Plane:

由于必须保证在参数域上,Wire 的方向是逆时针的,所以应当使用 Reversed 的 Edge0,Forward 的 Edge2,Forward 的 Edge1 构成 Wire。
如果使用了顺时针的 Wire ,即 Forward 的 Edge0,Reversed 的 Edge1,Reversed 的 Edge2,那么 Face 会定义为 Wire 不围成的部分。以下分别为逆时针和顺时针的 Wire:

如果 Geom3Plane 是用 Frame3(O, -OZ, OX) 构造的,那么 Wire 的方向应为顺时针方向,即 Forward 的 Edge0,Reversed 的 Edge1,Reversed 的 Edge2,这样就可以确保 Face 被正确定义为 Wire 围成的区域。
Wire 的 Reversed 等价于将 Forward 的 Wire 中的每个 Edge 的 Orientation 变为反向。
对 Face 进行 Reversed 后, Face 所包围的方向变为曲面法向的反向。对 Face 进行 Reversed 等价于将 Forward 的 Face 中 Wire 的 Orientation 变为反向。
其中获取 Face 所在曲面的法向的方法如下:
对 Shell 进行 Reversed 后 ,Shell 所包围的方向变为反向。对 Shell 进行 Reversed 等价于将 Forward 的 Shell 中的每个 Face 的 Orientation 变为反向。
对 Solid 进行 Reversed 后, Solid 所包围的方向变为反向。对 Solid 进行 Reversed 等价于将 Forward 的 Solid 中的每个 Face 的 Orientation 变为反向。
Tolerance 是表示某个 TopoShape 误差的量,比如一个 Vertex 在 Edge1 的曲线上的点是 Point3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0),在 Edge2 的曲线上的点是 Point3(1.0, 0.0, 0.0),在 tolerance=2.0 的情况下,这两个点可以视为一个点,也就是说这样的 Vertex 尽管在不同的 Edge 上的几何点不同,但作为拓扑结构,这个 Vertex 是合法的。
获取 TopoShape 的 Tolerance 的方法是:AMCAX::TopoTool::Tolerance()。只有 Vertex、Edge、Face 这种包含了几何信息的结构才有 Tolerance。而更改 Tolerance 的方法是: AMCAX::TopoBuilder::UpdateVertex() , AMCAX::TopoBuilder::UpdateEdge(), AMCAX::TopoBuilder::UpdateFace()。
接下来我们将逐一介绍 Vertex、Edge、Face 中的 Tolerance:
Vertex 的 Tolerance 是一个设定的值,其意义为 Point 到 Vertex 的距离(Point 到 Vertex 中 Point 的距离)不大于 Tolerance 时,认为 Point 在 Vertex 上。而 Vertex 的 Point 有很多来源:本身的 Point3,Curve 在某一参数上的值,Surface 在某一 uv 参数上的值,Vertex 的 Tolerance 要不小于这些点之间的最大距离。
Edge 的 Tolerance 是一个设定的值,其意义为 Point 到 Edge 的距离不大于 Tolerance 时,认为 Point 在 Edge 上。此外,Edge 有 curve3d 和 pcurve,而 pcurve 可以通过 Surface 构建一个等价的 curve3d。若干条 curve3d 在采样下的最大距离不能大于 Edge 的 Tolerance,如果不满足则必须增大 Edge 的 Tolerance。另外,Vertex 的 Tolerance 必须比所在 Edge 的 Tolerance 更大或相等。

Face 的 Tolerance 是一个设定的值,其意义为 Point 到 Face 的距离不大于 Tolerance 时,认为 Point 在 Face 上,较多用于布尔操作里。除此之外,Vertex、Edge 的 Tolerance 必须比所在 Face 的 Tolerance 更大或相等。
注:当存在从属关系时,Vertex 的 Tolerance ≥ Edge 的 Tolerance ≥ Face 的 Tolerance。
TopoShape 是否封闭是一个关键的 Flag。我们可以使用 AMCAX::TopoTool::IsClosed() 来判断 TopoShape 是否为封闭的。在这里需要与 AMCAX::TopoShape::Closed() 进行区分, AMCAX::TopoShape::Closed() 返回的 bool 是一个用户任意定义的 flag。比如,将一条线段构建成一个 Edge,尽管不封闭,但仍然可以用 AMCAX::TopoShape::Closed(true) 将其 flag 设为 true。
而 AMCAX::TopoTool::IsClosed() 是对某几类 TopoShape 进行拓扑上的判断。接下来将逐一介绍输入不同 ShapeType 的 TopoShape 时, AMCAX::TopoTool::IsClosed 的用途。
AMCAX::TopoTool::IsClosed() 用于判断 Edge 的 FirstVertex 和 LastVertex 是否 IsSame。
AMCAX::TopoTool::IsClosed() 用于判断 Wire 是否没有边界 Vertex,即对 Wire 遍历 Vertex,每个 Vertex 都出现偶数次。
AMCAX::TopoTool::IsClosed() 用于判断 Shell 是否没有边界 Edge(自由Edge),即对 Shell 遍历 Edge,除退化边外每个 Edge 都出现偶数次。
对 edge wire shell 外的其他类型执行 AMCAX::TopoTool::IsClosed() 时,其结果就是 AMCAX::TopoShape::Closed() 的结果。