Overview
This tutorial provides the basic usage of geometry editing, including importing brep format files and performing geometric editing operations on the model using the GeomE API for model repair. The tutorial also utilizes the API from the AMCAX kernel. Additionally, in the images of this tutorial, the red edge represents free edge, while the yellow edge represents manifold edge.
Namespace
To keep the example code clear, namespaces are used.
Namespace of all interface in the AMCAX GeomE module.
Definition misc.docu:21
Namespace of all interface in the AMCAX kernel.
Definition misc.docu:8
Geometry Edit example one
CAD Model Preview
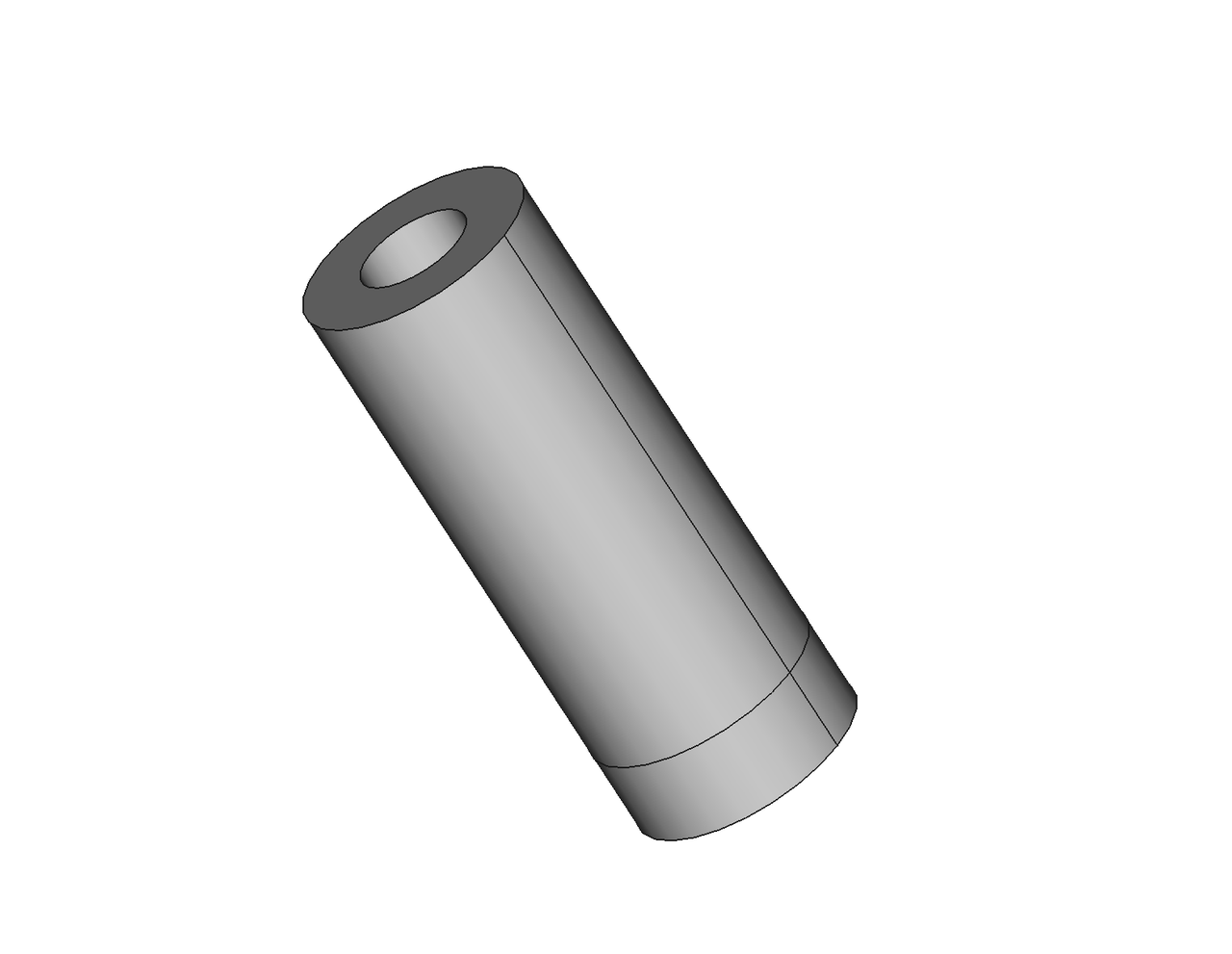
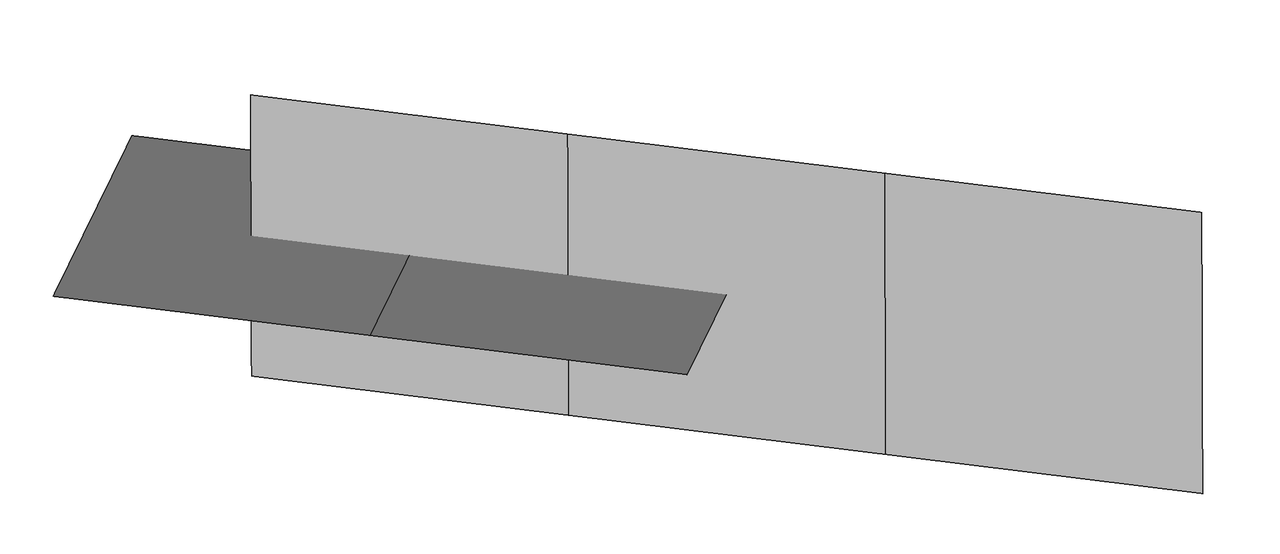
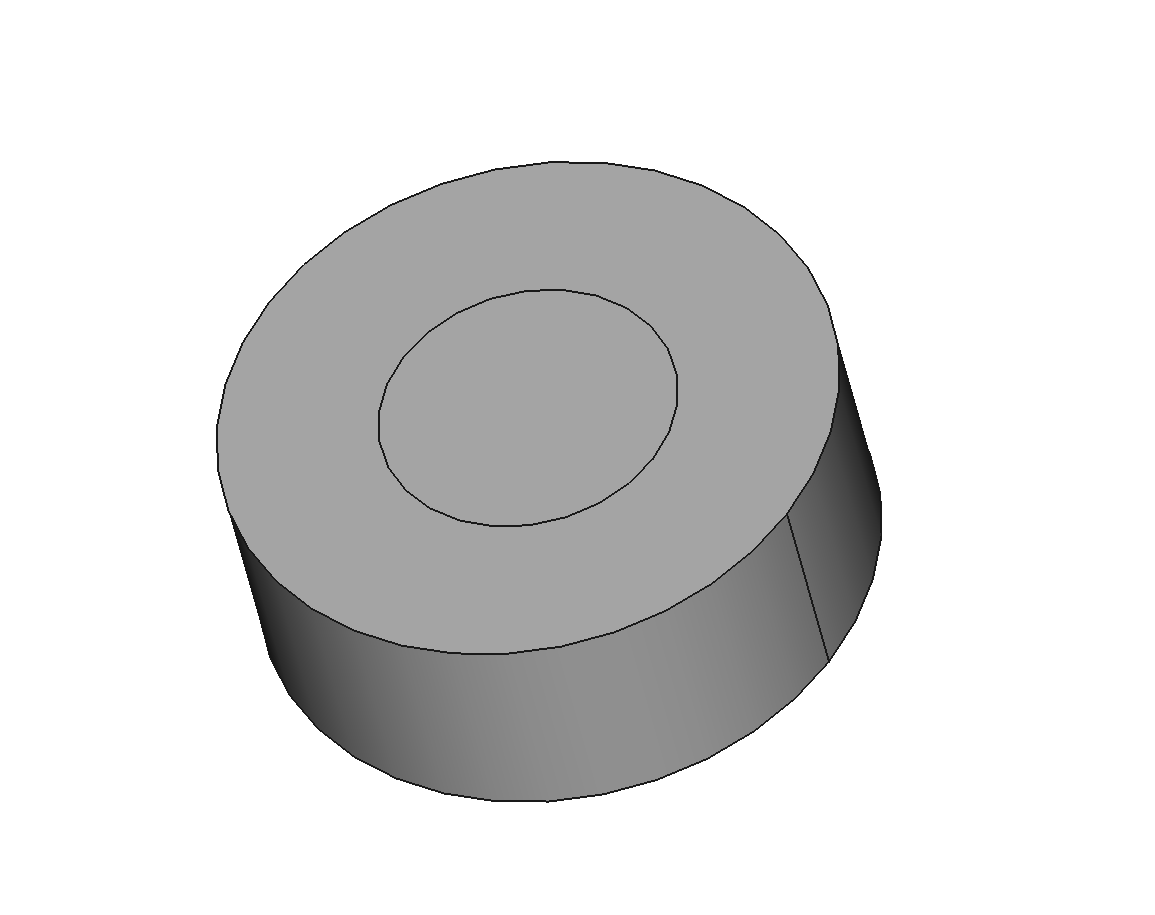
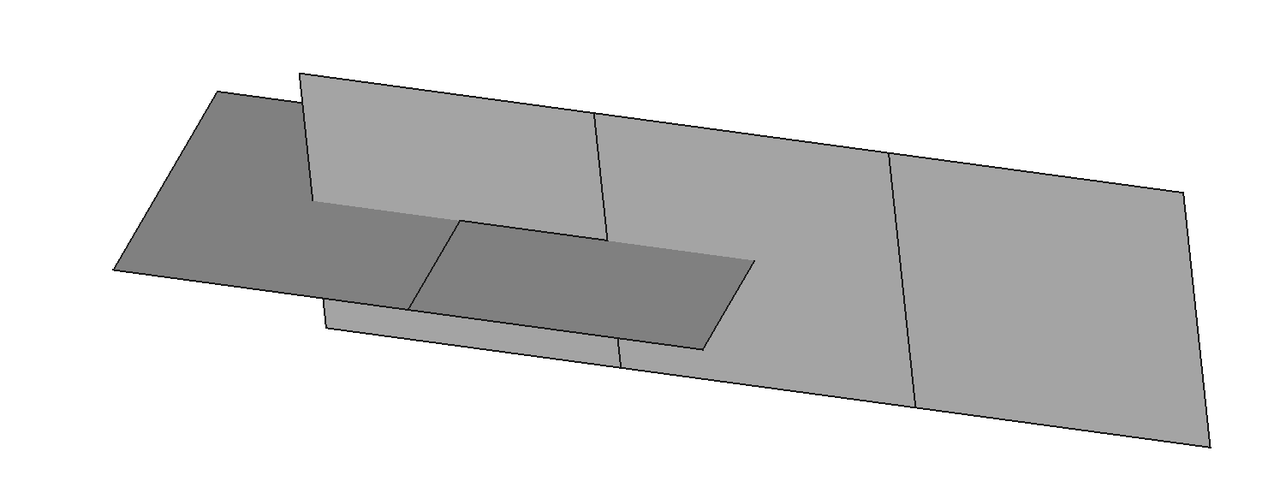
Import a brep format CAD model, as shown in the figure below:
Preparation
This tutorial example will first read in a brep model, then perform geometric editing operations on the input model, and finally write the model into a BREP file.
Header Files
Import Model
Import the CAD file and construct the model.
Base class of shape, containing an underlying shape with a location and an orientation.
Definition TopoShape.hpp:15
Output Result
Write to brep file.
As shown in the figure, the area marked with a red circle has a gap between the short edge of one face and the long edge of another face. Both edges are free edges.
Point insertion into edge
static AMCAX_API void TrimEdgeWithPoint(TopoShape &shape, const TopoEdge &edge, const std::vector< Point3 > &points)
Project points onto an edge.
Template class of indexed set.
Definition IndexSet.hpp:20
static AMCAX_API const TopoEdge & Edge(const TopoShape &s)
Cast shape to edge.
static AMCAX_API const TopoVertex & Vertex(const TopoShape &s)
Cast shape to vertex.
Class of edge.
Definition TopoEdge.hpp:12
Class of vertex.
Definition TopoVertex.hpp:12
PointT< double, 3 > Point3
3D point
Definition PointT.hpp:459
As shown in the figure, the point has been inserted into the corresponding edge, and the long edge has been split into two edges.
Sew one edge onto another edge
static AMCAX_API void SewEdges(AMCAX::TopoShape &shape, const AMCAX::TopoEdge &edge1, AMCAX::TopoEdge &edge2, double tol)
Sew two edges with nearby vertices, using the second edge as the resulting edge.
void clear() noexcept
Clear the indexed set.
Definition IndexSet.hpp:90
As shown in the figure, the gap between the two faces has been eliminated.
As shown in the figure, the area marked with a red circle has a gap between the edge of one face and another face.
Project the edge onto the face
static AMCAX_API void EdgesProjectFace(TopoShape &shape, const IndexSet< TopoShape > &edges, TopoFace &face, TopoShape &replaceshape)
Project edges onto a surface.
int insert(T &&key)
Insert a new key.
Definition IndexSet.hpp:102
static AMCAX_API const TopoFace & Face(const TopoShape &s)
Cast shape to face.
Class of face.
Definition TopoFace.hpp:12
As shown in the figure, the specified edge has been projected onto the interior of the face.
Sew one edge to another edge
As shown in the figure, in the area marked with a red circle, a very short edge has appeared.
Release the Vertex
static AMCAX_API void ReleaseVertex(TopoShape &shape, const TopoVertex &vertex)
Release vertex onto each edge.
As shown in the figure, the vertex has been released onto the respective faces.
Delete the Vertex
Delete the red vertex of the star-shaped marked face.
static AMCAX_API void RemoveVertex(TopoShape &shape, const TopoVertex &vertex)
Delete vertex on the edge.
As shown in the figure, the red vertex of the star-shaped marked face has been deleted, and the long edge and short edge are now connected as a single edge.
Sew the Vertex
As shown in the figure, the vertex of the face on the right needs to be sewn to the vertex of the face on the left.
static AMCAX_API TopoVertex SewVertices(AMCAX::TopoShape &shape, const IndexSet< TopoShape > &vertexvec)
Sew a set of vertices into a single vertex.
As shown in the figure, the two vertices have been sewn together.
Sew one edge to another edge.
As shown in the figure, the edge of the left face is stitched to the edge of the right face.
As shown in the figure, select the two vertices to perform parameter cut on the face.
Parameter Cut
static AMCAX_API void ParameterFaceCut(AMCAX::TopoShape &shape, const AMCAX::TopoFace &face, const AMCAX::TopoVertex &vertex1, const AMCAX::TopoVertex &vertex2)
Parametrically cut the given face using the specified pair of vertices.
As shown in the figure, the parameter cut was successful.
Rebuild the edge
As shown in the figure, you can select an edge (yellow) for rebuilding.
static AMCAX_API TopoEdge RebuildAndUpdateEdge(TopoShape &shape, const TopoEdge &edge)
Resample the curve of an edge and update it.
The following are the edge before rebuilding and the edge after rebuilding.
Insert a vertex on the edge based on the ratio.
As shown in the figure, insert a vertex at a ratio of 0.3 on the selected edge (yellow).
static AMCAX_API void TrimEdgeWithRatio(TopoShape &shape, const TopoEdge &edge, const std::vector< double > &ratios)
Insert vertices on the edge based on the given ratios.
As shown in the figure, a vertex has been inserted at 0.3 of the selected edge.
Release the edge
As shown in the figure, release the edge circled in red.
static AMCAX_API void ReleaseEdge(AMCAX::TopoShape &shape, const AMCAX::TopoEdge &edge)
Release the common edge of several faces to their respective faces.
As shown in the figure, the selected edge has been released onto two faces, becoming free edges.
Delete the face
As shown in the figure, the star-marked face needs to be deleted.
static AMCAX_API void DeleteFace(AMCAX::TopoShape &shape, const AMCAX::TopoFace &face)
Remove a face from the shape.
As shown in the figure, the selected face has been deleted.
Join two edges into one edge
As shown in the figure, join the two red edges.
static AMCAX_API TopoEdge JoinEdgesAndUpdate(AMCAX::TopoShape &shape, const IndexSet< TopoShape > &edges)
Join edges into one edge.
As shown in the figure, after the joint, the two edges become one edge, and the vertex disappears.
Reverse the orientation of the face
static AMCAX_API void ReverseOrientation(AMCAX::TopoShape &shape, const AMCAX::TopoFace &face)
Reverse the orientation of a face.
Click here example01 to get the full source code of the geometry edit example one. Everyone can download it as needed.
Appendix
The complete code for this example is listed below:
Geometry Edit example two
CAD Model Preview
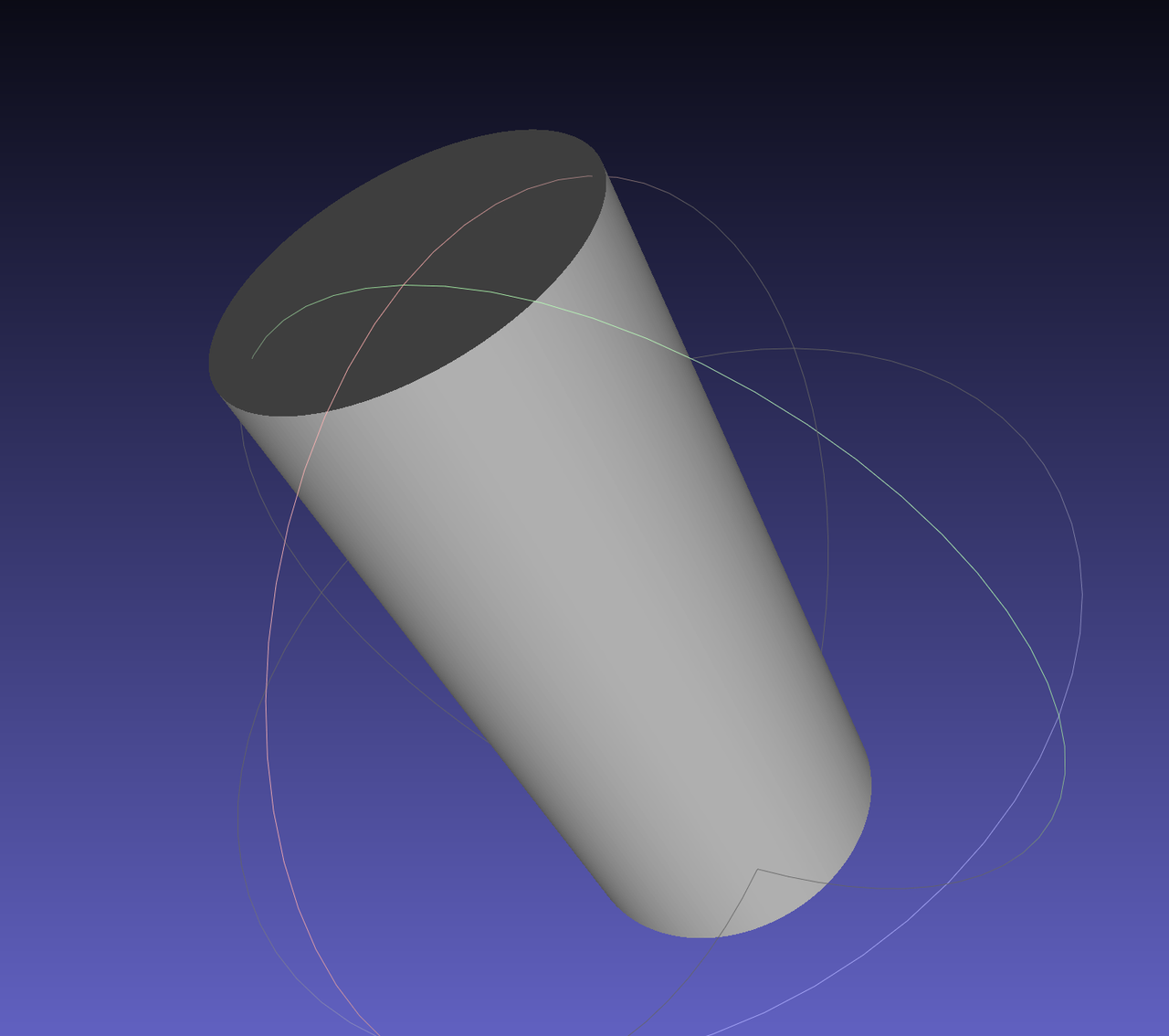
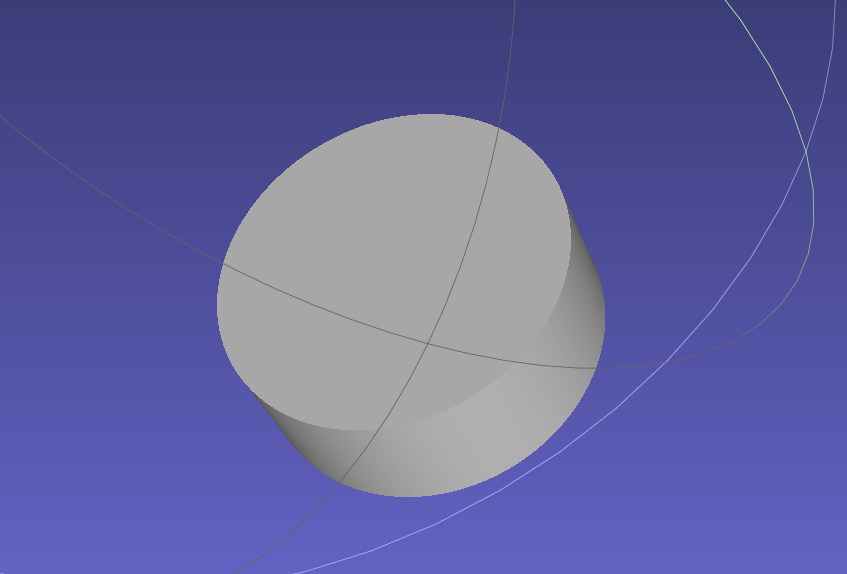
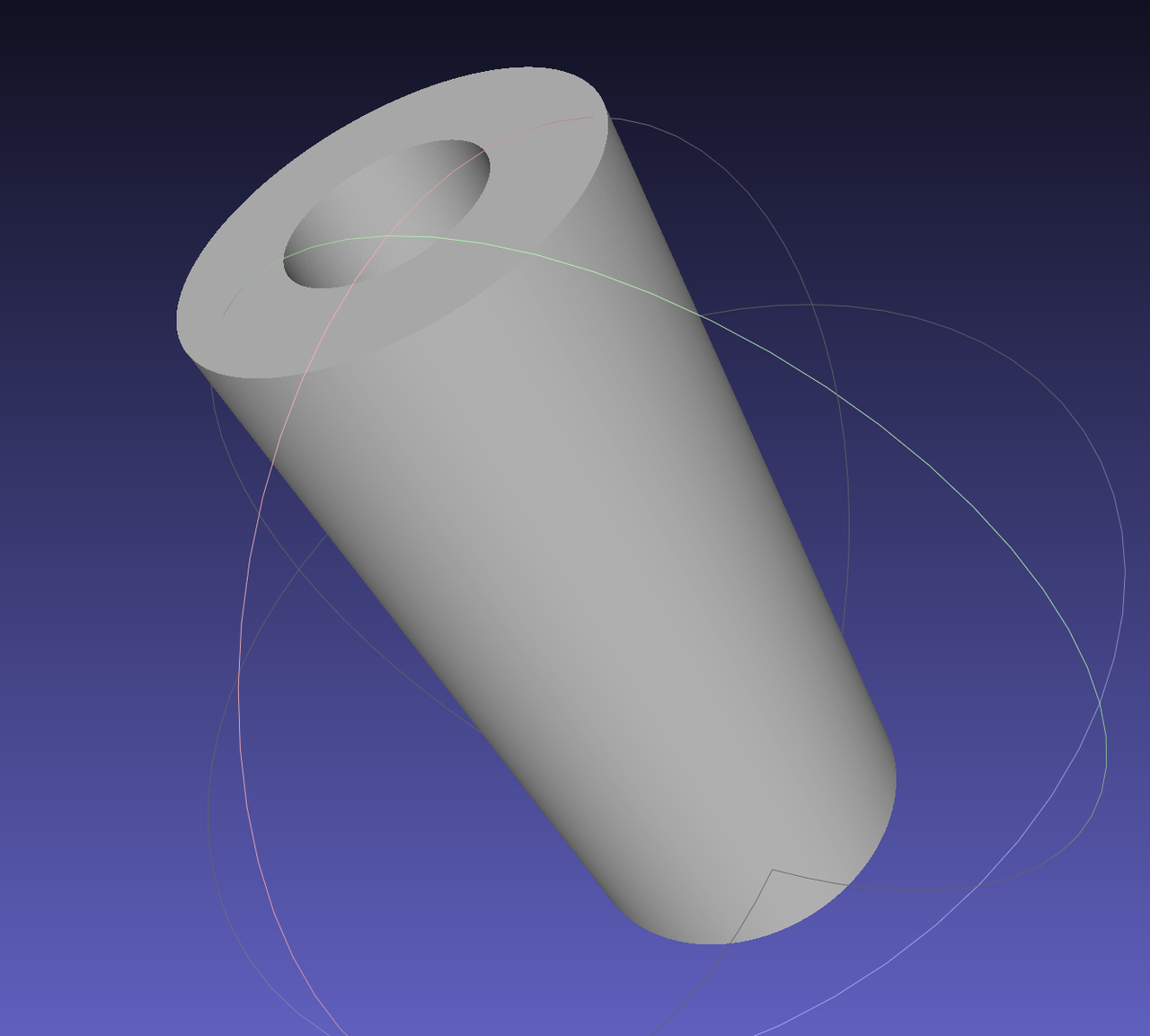
Import a STEP format CAD model, as shown in the figure below:
Preparation
In this tutorial example, the STEP model will first be read in, followed by geometric editing operations on the input model, and finally, the model will be written to a BREP file.
Relevant Header Files
Class of making a vertex.
Import Model
Import the CAD file and build the model.
Output Result
Write the model to a BREP file.
Detect Edge Type
EdgeType
Type of edges.
Definition GeomEMacros.hpp:12
As shown in the figure, the green edge is selected for detection. The returned EdgeType for this edge is FreeEdge, indicating that this edge is a free edge.
Detect Free Boundaries of the Edge
As shown in the figure, the free boundary containing the edge is detected.
Fill Holes in the Free Boundary
static AMCAX_API void FillHole(TopoShape &shape, const IndexSet< TopoShape > &freeboundaries)
Fill the holes formed by free boundaries.
As shown in the figure, the hole bounded by the free boundary has been filled.
Create a New Coons Surface from the Selected Boundary
As shown in the figure, the green edges are selected as a set to construct a new plane.
static AMCAX_API TopoFace BuildCoons(TopoShape &shape, const IndexSet< TopoShape > &edges)
Construct a new coons face based on the given set of edges.
As shown in the figure, the Coons Surface has been successfully constructed.
Create a New Plane from the Selected Boundary
As shown in the figure, the green edges are selected as a set to construct a new plane.
static AMCAX_API TopoFace BuildPlane(TopoShape &shape, const IndexSet< TopoShape > &edges)
Construct a new plane face based on the given set of edges.
As shown in the figure, the plane has been successfully constructed.
Create a New Face Based on an Existing Surface
As shown in the figure, the green edges are selected as a set to create a new face based on the surface of the yellow face.
static AMCAX_API TopoFace BuildFaceFromSurface(TopoShape &shape, const IndexSet< TopoShape > &edges, const TopoFace &face)
Construct a new face based on the given set of edges and an existing face.
As shown in the figure, the new face has been successfully created.
Project a Point onto a Face
static AMCAX_API void VerticesProjectFace(TopoShape &shape, const IndexSet< TopoShape > &vertices, TopoFace &face, TopoShape &replaceshape)
Project vertices onto a surface.
Class of making a vertex.
Definition MakeVertex.hpp:16
As shown in the figure, the point has been successfully projected onto the face.
Click here example02 to get the full source code of the geometry edit example two. Everyone can download it as needed.
Appendix
void GeomEdit()
{
shape, "./data/skin.step");
}
Geometry Edit example three
CAD Model Preview
Import a BREP format CAD model as shown in the following images. The left image is the initial model 1, and the right image is the initial model 2.
Preparation Work
In this tutorial, the example first reads in a BREP model, then performs geometric editing operations on the input model, and finally writes the model into a BREP file.
Relevant Header Files
Class of Geometric Imprinting.
Defines data structures for configuration options across various functionalities.
Base class of shape, containing an underlying shape with a location and an orientation.
Importing the Model
Import the CAD file and construct the model.
Output Results
Write the BREP.
Geometry Editing Example
Consistent Face Orientation
The initial model 1 consists of two solids, with the faces of the first solid having inconsistent orientations.
static AMCAX_API void AlignFaceOrientations(TopoShape &shape)
Ensure consistent orientation of all faces in a shape without non-manifold edges.
As shown in the image below, after performing face orientation alignment on the first solid, the normal vectors of all faces are directed outward.
Check if the Shell is Closed
Check if the shell of the first solid is closed, return true.
Geometric Imprint 1
imprint1.
Imprint(shape, {solids[0], solids[1]}, {});
Class of Geometric Imprinting.
Definition GeomImprint.hpp:23
AMCAX_API void Imprint(TopoShape &shape, const std::list< TopoShape > &targetlist, const std::list< TopoShape > &toollist={}, const ImprintOptions &options=ImprintOptions())
Performs mutual imprinting of multiple shapes or imprints a list of faces onto another list of faces.
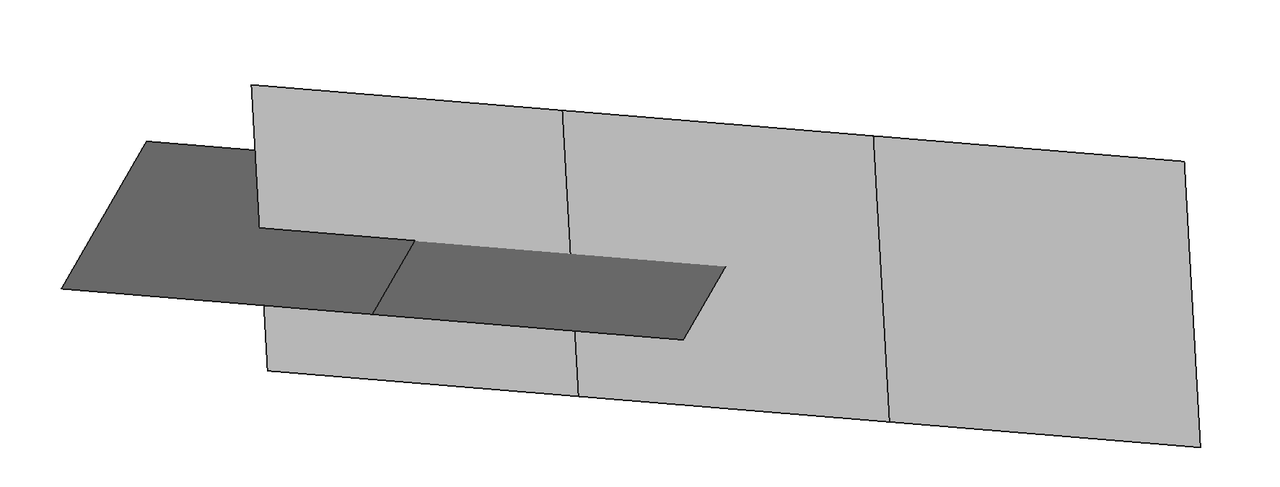
As shown in the image below, the second solid has been imprinted with some topological structures.
Geometric Imprint 2
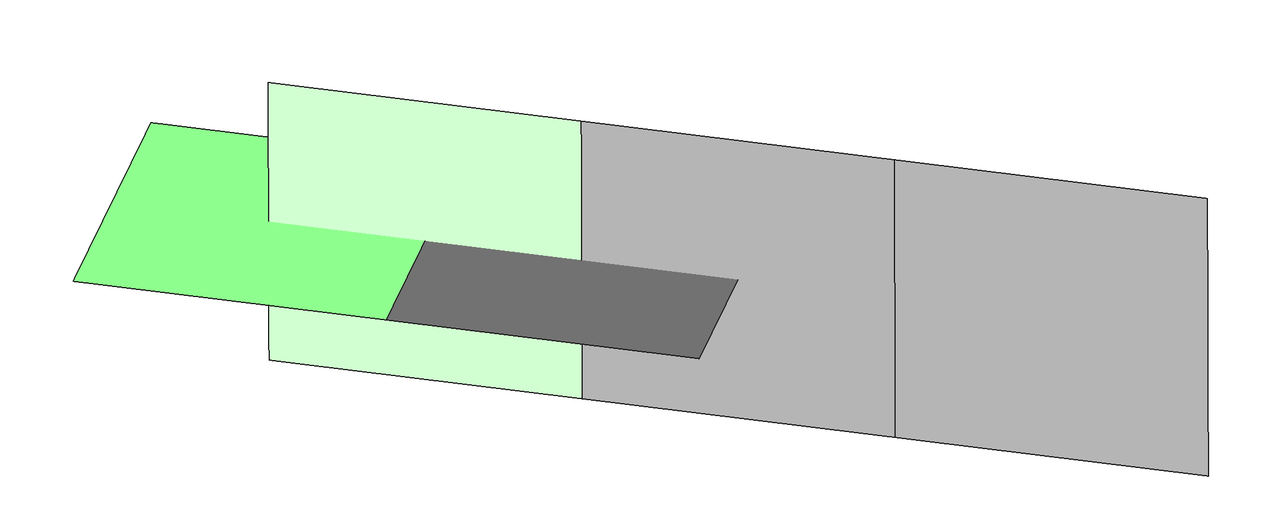
As shown in the image below, select the green face for geometric imprinting.
imprint2.
Imprint(shape, {faces[0]}, {faces[2]});
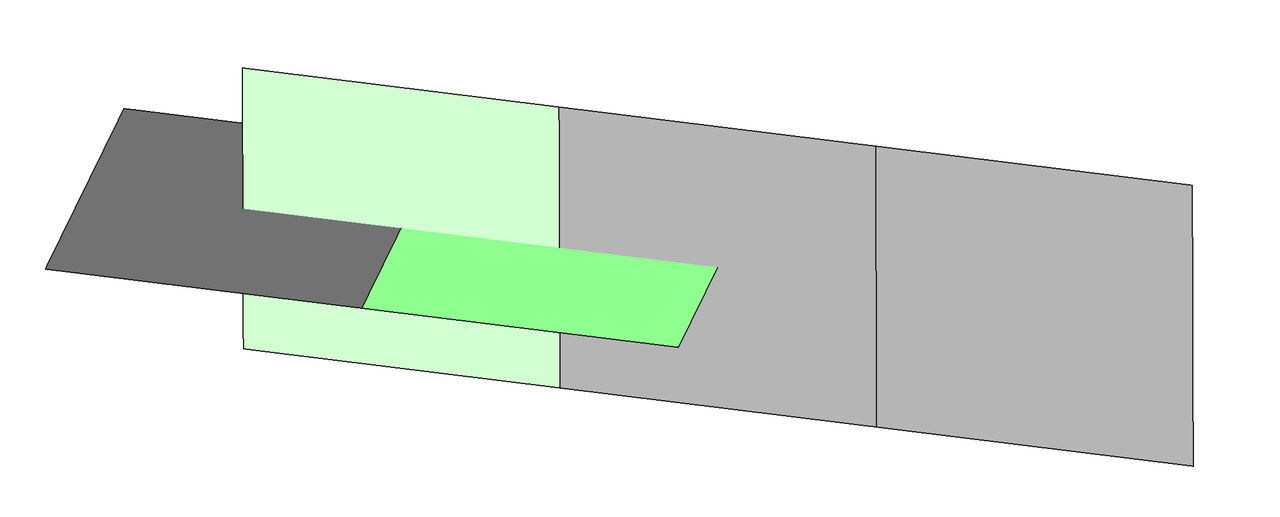
As shown in the image below, the imprint was successful.
Geometric Imprint 3
As shown in the image below, select the green face for geometric imprinting.
imprint3.
Imprint(shape, {faces[1]}, {faces[2]});
As shown in the image below, the imprint was successful.
Click here example03 to get the full source code of the geometry edit example three. Everyone can download it as needed.
Appendix
void GeomEditor()
{
imprint1.
Imprint(shape, {solids[0], solids[1]}, {});
imprint2.
Imprint(shape, {faces[0]}, {faces[2]});
imprint3.
Imprint(shape, {faces[1]}, {faces[2]});
}