Overview
This tutorial outlines the basic usage of mesh generation. It involves the process of importing STEP format files and automatic generation of the volumetric mesh, which is controlled by parameters specified by a JSON file.
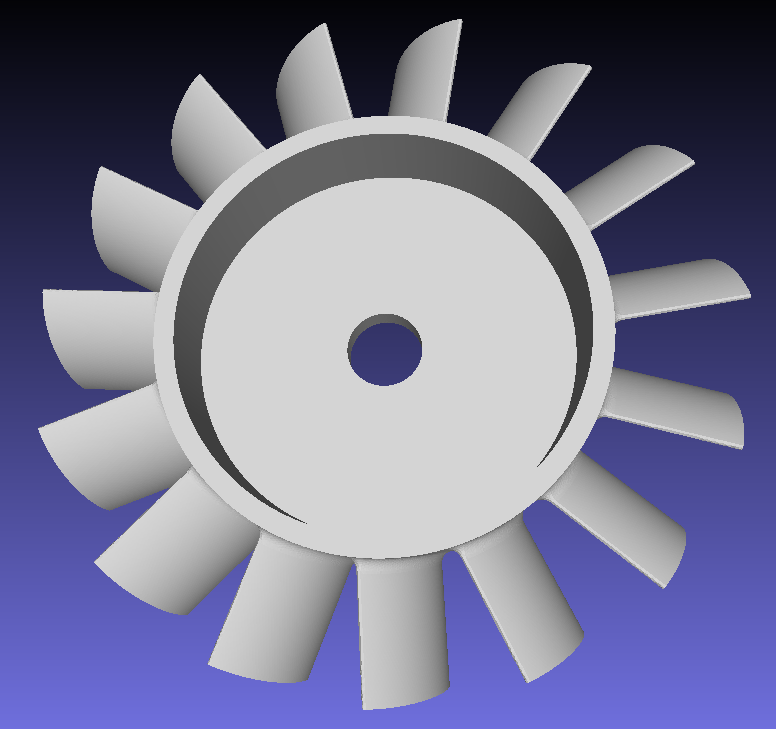
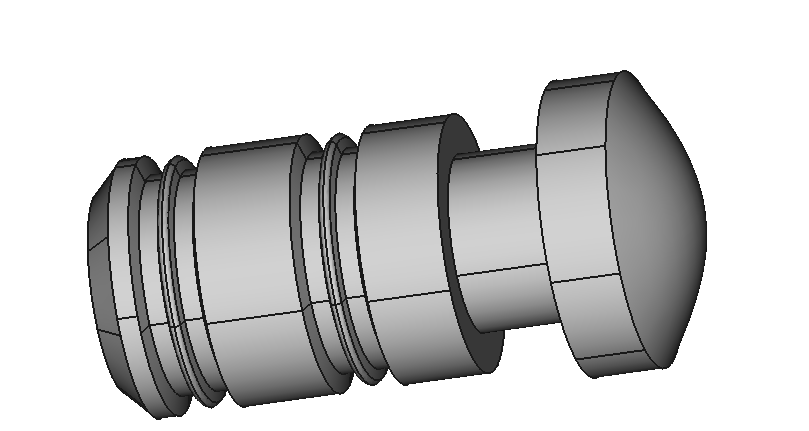
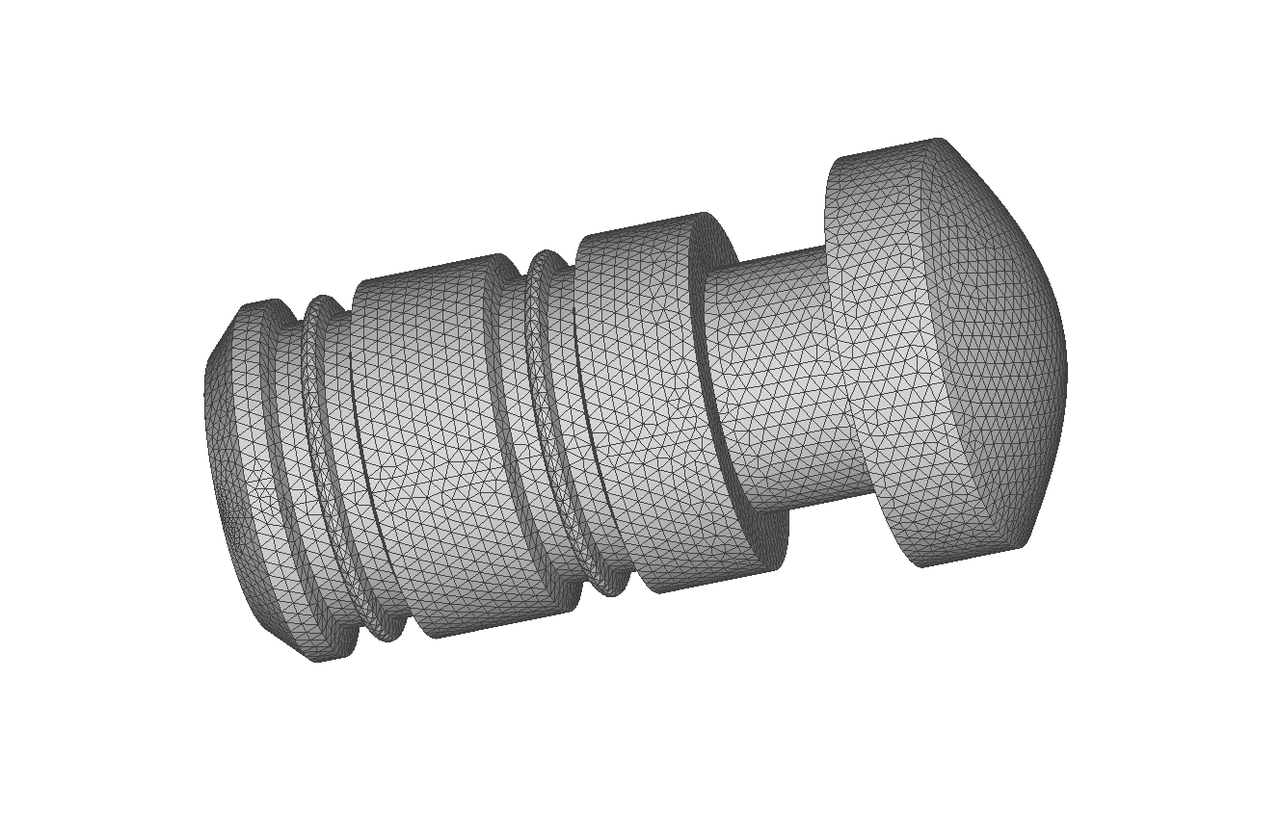
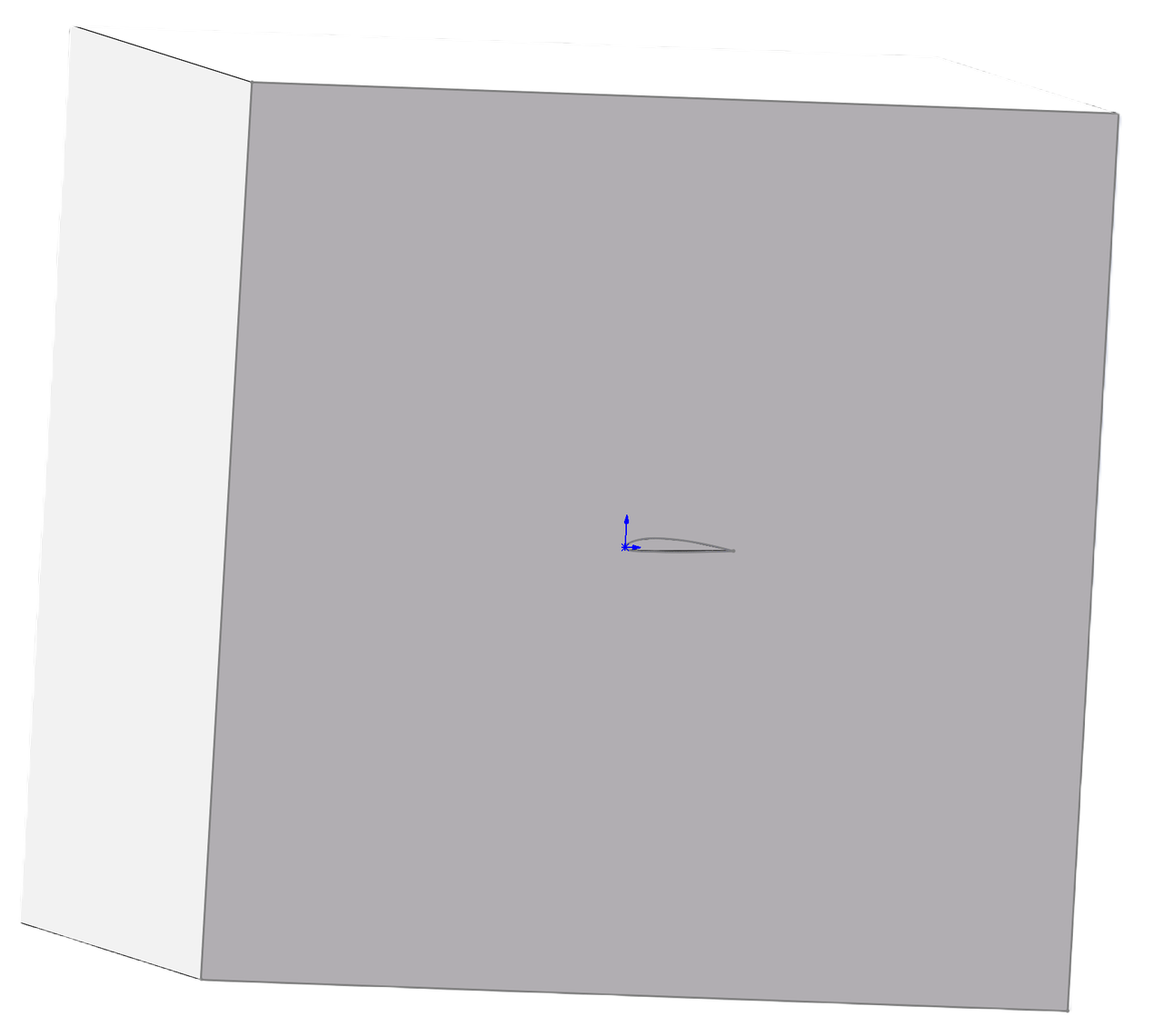
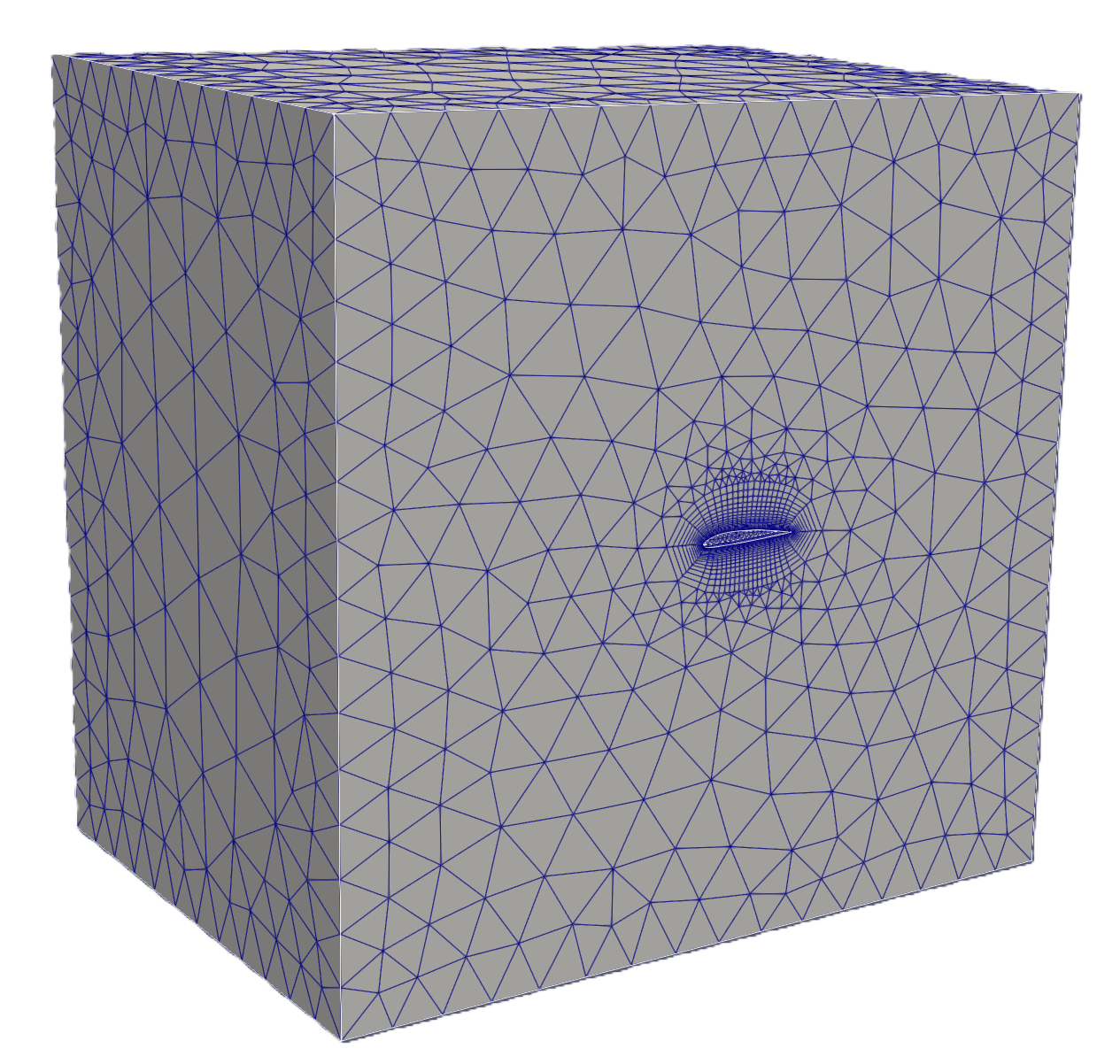
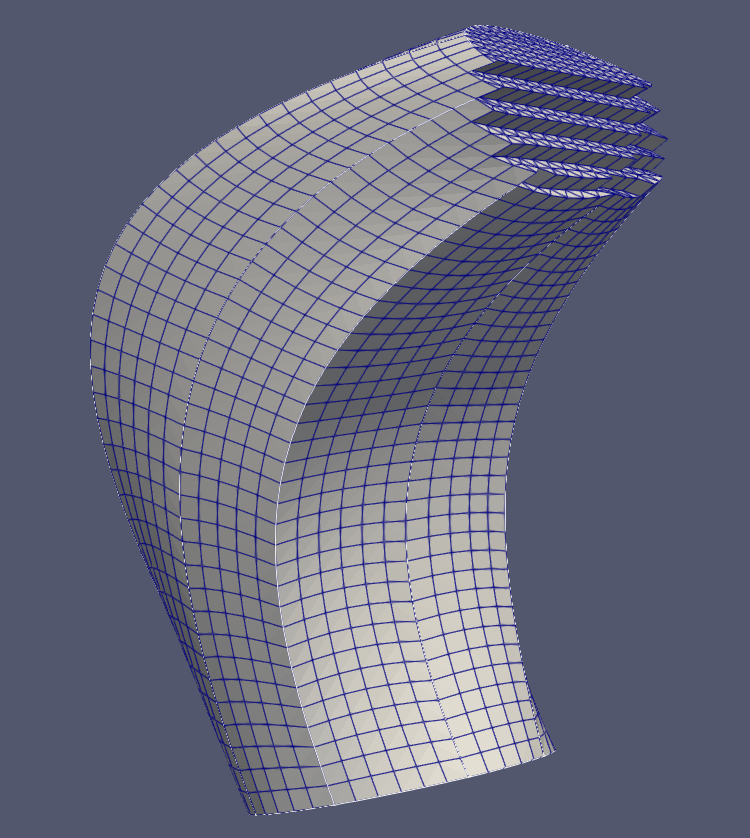
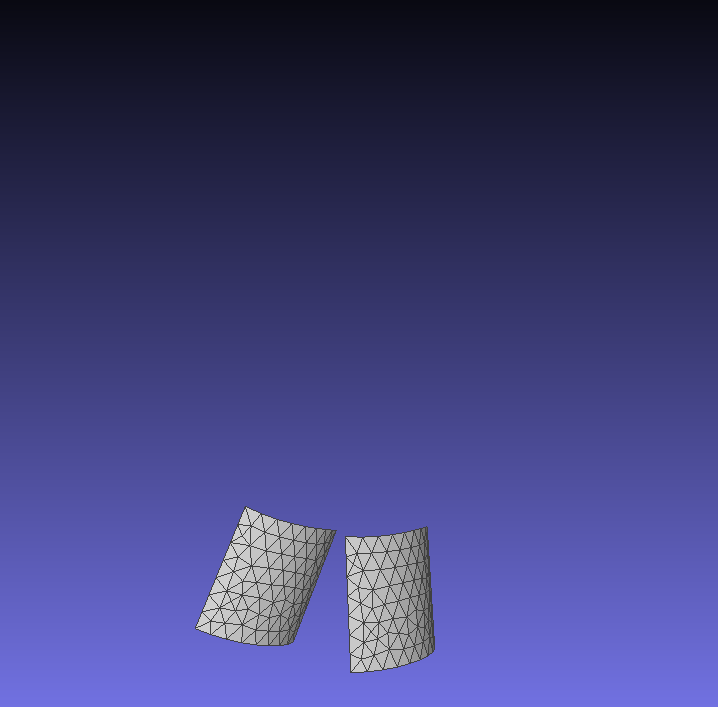
Preview of CAD Model and the generated mesh
The left image shows the imported CAD model, while the right image displays the final generated mesh model.
Namespaces
Namespace of all interface in the AMCAX NextMesh module.
Definition: misc.docu:42
Preparation
Set the log format, provide the cad file and the mesh generation control JSON file.
const std::string cadstr = "./data/qiuwotaojian.stp";
const std::string jsonPath = "./data/mesh_para-mesh000.json";
NMAPIModel::InitLogger();
Json example
The mesh size is controlled by setting the following parameters: "MeshingDim" (1-3), the dimension of the entity for partitioning; "MaxSize"/"MinSize" (absolute size), the maximum and minimum size of the mesh element, which can be obtained by multiplying the length of the diagonal of the model boundingbox (bblen) by a ratio (r), e.g. [0.01, 0.1]*bblen; "GrowthRate" (>=1.0), the growth rate of Mesh size ; "SelectedEntities", the tags of the entities for partitioning (null value indicates all entities under the specified dimension); "CurvatureFactor" (0.0-1.0), curvature factor ; "ThreadNum", number of parallel threads.
{
"MeshSize": [
{
"CurvatureFactor": 0.6,
"GrowthRate": 1.0,
"MaxSize": 0.5,
"MeshingDim": 3,
"MinSize": 0.1,
"SelectedEntities": []
}
],
"ThreadNum": 1
}
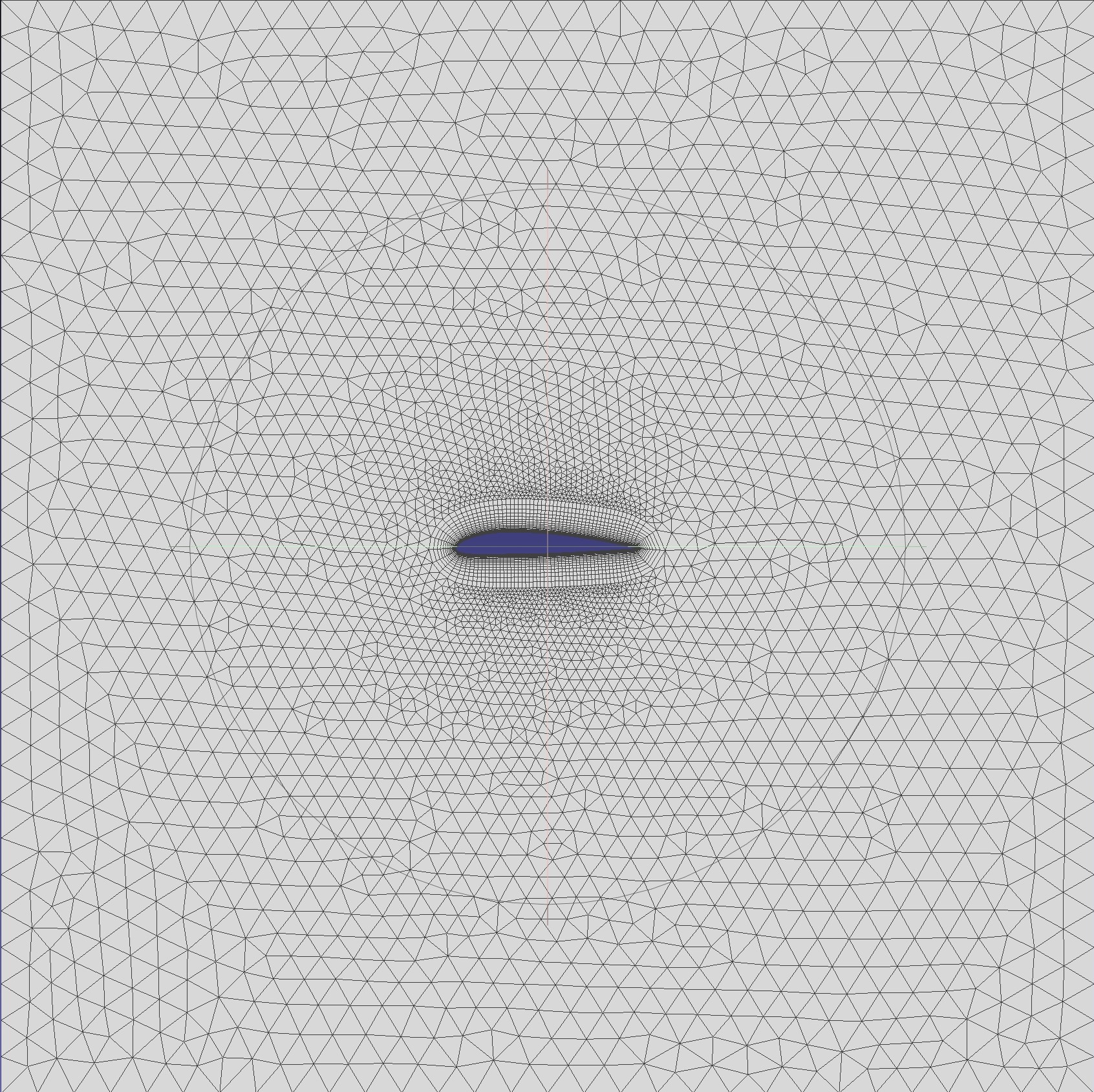
JSON example - Planar boundary layer
This example generates a planar boundary layer hybrid mesh for a two-dimensional airfoil.
{
"BoundaryLayer": [
{
"DistributionType": "Separation",
"EntityType": "Edge",
"EFPairs": [
{
"E": 5,
"F": 1
},
{
"E": 6,
"F": 1
}
],
"Basic": {
"GrowthRate": {
"Constant": 1.2
},
"InitLayerHeight": {
"Absolute": 0.01
},
"NLayers": 20,
"ProblematicAreasTreatment": "STOP"
}
}
],
"MeshSize": [
{
"CurvatureFactor": 0.2,
"GrowthRate": 1.1,
"MaxSize": 0.2,
"MeshingDim": 1,
"MinSize": 0.1,
"SelectedEntities": [ 5, 6 ]
},
{
"CurvatureFactor": 0.2,
"GrowthRate": 1.0,
"MaxSize": 2,
"MeshingDim": 2,
"MinSize": 1,
"SelectedEntities": []
}
],
"ThreadNum": 1
}
The following are the imported CAD model and the final generated mesh model.
For more complex configurations, please refer to 2D Boundary Layer Detailed JSON Example
JSON Example - Spatial boundary layer
This example generates a spatial boundary layer hybrid mesh for a three-dimensional airfoil.
{
"Distribution": [],
"BoundaryLayer": [
{
"DistributionType": "Separation",
"EntityType": "Edge",
"EFPairs":
[
{
"E": 2,
"F": 7
},
{
"E": 17,
"F": 7
}
],
"Basic":
{
"GrowthRate":
{
"Constant": 1.2
},
"InitLayerHeight":
{
"Absolute": 0.002
},
"NLayers": 20,
"ProblematicAreasTreatment": "STOP"
}
},
{
"GrowthRate": 1.2,
"InitLayerHeight": 0.002,
"NLayers": 20,
"DistributionType": "Separation",
"SelectedEntities": [ 1, 8, 9 ],
"EntityType": "Face"
}
],
"MeshSize": [
{
"CurvatureFactor": 0.2,
"GrowthRate": 1.3,
"MaxSize": 0.2,
"MeshingDim": 1,
"MinSize": 0.1,
"SelectedEntities": [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 17, 18 ]
},
{
"CurvatureFactor": 0.2,
"GrowthRate": 1.1,
"MaxSize": 5,
"MeshingDim": 2,
"MinSize": 1,
"SelectedEntities": [ 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ]
},
{
"CurvatureFactor": 0.2,
"GrowthRate": 1.1,
"MaxSize": 5,
"MeshingDim": 2,
"MinSize": 0.1,
"SelectedEntities": [ 1, 8, 9 ]
},
{
"CurvatureFactor": 0.2,
"GrowthRate": 1.1,
"MaxSize": 5,
"MeshingDim": 3,
"MinSize": 1,
"SelectedEntities": []
}
],
"ThreadNum": 1
}
The following are the imported CAD model and the final generated mesh model, along with the section view.
JSON example - Sweep mesh
Sweep meshing only supports a single sweep body, the source surface may consist of multiple faces, while the target surface can only include a single face. The side faces must be either 2-sided, 3-sided, or 4-sided faces.
{
"Sweep": [
{
"EntityType": "Face",
"Domain": 1,
"Source": [9],
"Target": [10]
}
],
"MeshSize": [
{
"CurvatureFactor": 0.2,
"GrowthRate": 1.0,
"MaxSize": 1,
"MeshingDim": 3,
"MinSize": 0.1,
"SelectedEntities": []
}
],
"ThreadNum": 1
}
The following are the imported CAD model and the generated mesh model.
JSON Example - Copy mesh
You can copy the mesh of a single or multiple Entity (edge or face) onto a single target Entity. This is applied in scenarios where the mesh topology of the source and target must match exactly, such as in periodic mesh. Notes: The source can contain multiple Entity, but the target can only contain one Entity; The topological structure of the source and target must be identical; When copy face mesh, the correspondence of boundary edges must be correctly specified.
{
"Copy": [
{
"EntityType": "Face",
"Source": [1, 2],
"Target": [3],
"EdgeCorrespondence":
[
{
"Source": [ 1, 2, 3 ],
"Target": [ 4 ]
},
{
"Source": [ 7 ],
"Target": [ 6 ]
}
]
},
{
"EntityType": "Edge",
"Orientation": "Forward",
"CopyType":"Uniform",
"Source": [1, 2],
"Target": [3]
},
]
}
Using "Entity" as a face, the following are the imported CAD model and the copied mesh.
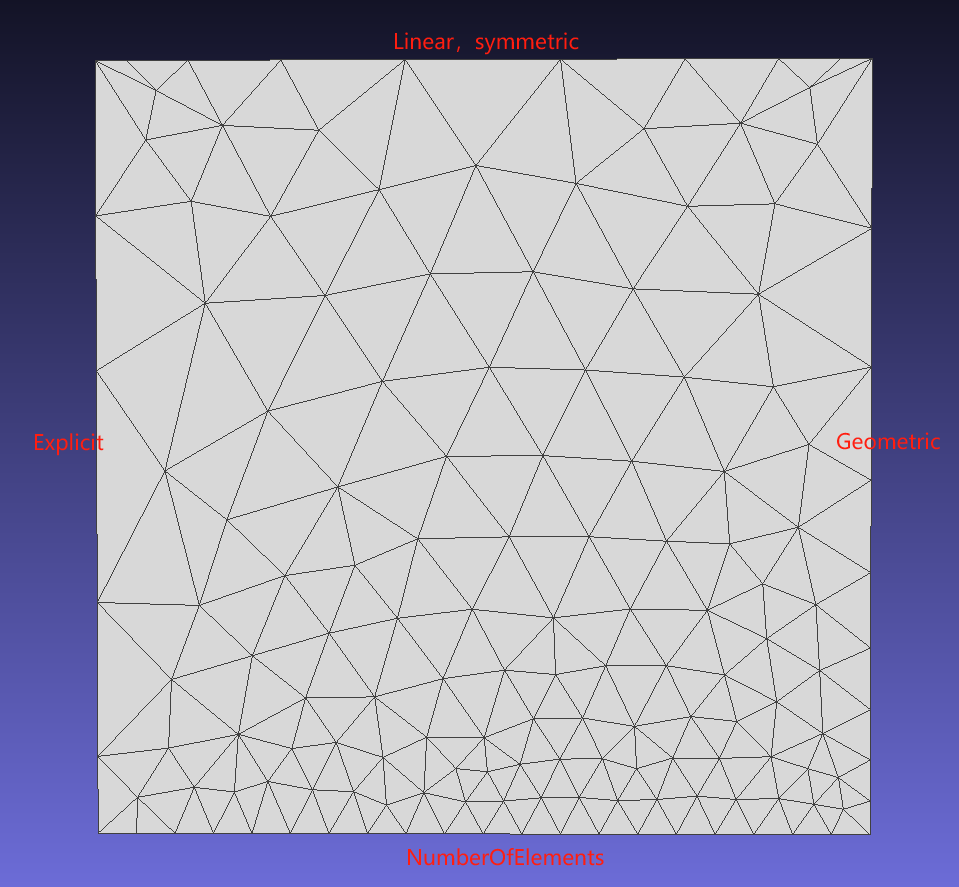
JSON Example - Multiple line mesh generation methods
Method 1: Specify the number of elements on an edge;
Method 2: Explicitly specify the length ratio of each segment of elements on the edge;
Method 3: Partition based on a pre-defined function (Linear/Geometric);
{
"Distribution": [
{
"EntityType": "Edge",
"SelectedEntities": [1, 2],
"DistributionType": "NumberOfElements",
"NElement": 20
},
{
"EntityType": "Edge",
"SelectedEntities": [4],
"DistributionType": "Explicit",
"Orientation": "Forward",
"DistributionPara": [0.1, 0.3, 0.6, 0.8]
},
{
"EntityType": "Edge",
"SelectedEntities": [3],
"DistributionType": "Linear",
"Orientation": "Forward",
"Symmetric": true,
"NElement":10,
"EndBeginElementRatio":3
}
]
}
| Class | Key | Required | Value Range | Default Value | Notes |
| Distribution | EntityType | Yes | Edge | – | |
| Distribution | SelectedEntities | Yes | Can be empty | – | Edge tags |
| Distribution | DistributionType | Yes | NumberOfElements, Explicit, Linear, Geometric | – | Distribution type |
| Distribution | Orientation | No | Forward, Reverse | Forward | Orientation |
| Distribution | Symmetric | No | true, false | false | Symmetric distribution |
| Distribution | NElement | Yes | >=1 | – | Number of segments |
| Distribution | EndBeginElementRatio | Yes | >0 | – | Ratio of the length of the last segment to the first segment |
| Distribution | DistributionPara | Yes | (0.0, 1.0) | – | Strictly increasing sequence |
The following are the results of various line mesh mesh generation methods.
Build the model
Import the cad file and build the model.
NMAPIModel nmapi;
nmapi.ImportModel(cadstr);
Generate/get mesh
generate mesh by importing mesh generation control parameter via JSON file.
nlohmann::json paraJ = nlohmann::json::parse(std::ifstream(jsonPath));
nmapi.GenerateMesh(paraJ.dump());
auto meshapi = nmapi.GetMesh();
Get mesh and geometry information
Get the model's entity list, the BRep (boundary representation) relationships of entities, and their boundingboxes. For each entity, obtain the types of meshes it contains, the mesh elements, vertices, and the global IDs of the mesh elements and vertices, along with other related information.
for (
DimType dim : {DimType::D0, DimType::D1, DimType::D2, DimType::D3})
{
std::vector<NMEntity> etVec;
nmapi.GetEntities(etVec, dim);
for (auto ent : etVec)
{
auto eTag = nmapi.EntityGetTag(ent);
auto dim = nmapi.EntityGetDim(ent);
std::vector<ElemType> typeVec;
meshapi.GetEntityElementTypes(typeVec, ent);
std::vector<NMEntity> parentVec;
nmapi.GetParentAdjacentEntities(parentVec, ent);
std::vector<NMEntity> childVec;
std::vector<Orientation> ories;
nmapi.GetChildAdjacentEntities(childVec, ories, ent);
auto entElemNum = meshapi.EntityGetElementCount(ent);
for (size_t i = 0; i < entElemNum; i++)
{
auto elem = meshapi.EntityGetElementByIndex(ent, i);
}
auto entNodeNum = meshapi.EntityGetNodeCount(ent);
for (size_t i = 0; i < entNodeNum; i++)
{
auto node = meshapi.EntityGetNodeByIndex(ent, i);
}
}
}
nmapi.GetBBox(pmin, pmax);
auto elemTotalNum = meshapi.GetElementCount();
for (size_t i = 0; i < elemTotalNum; i++)
{
auto elem = meshapi.GetElementByIndex(i);
auto elemId = meshapi.ElementGetID(elem);
auto elemType = meshapi.ElementGetType(elem);
auto nodeCount = meshapi.ElementGetNodeCount(elem);
for (size_t in = 0; in < nodeCount; in++)
{
auto node = meshapi.ElementGetNode(elem, in);
auto nodeId = meshapi.NodeGetID(node);
auto nodeEnt = meshapi.NodeGetEntity(node);
auto nodePos = meshapi.NodeGetPosition(node);
if (nmapi.EntityGetDim(nodeEnt) == DimType::D1 ||
nmapi.EntityGetDim(nodeEnt) == DimType::D2)
double u = meshapi.NodeGetFirstParameter(node);
if (nmapi.EntityGetDim(nodeEnt) == DimType::D2)
double v = meshapi.NodeGetSecondParameter(node);
}
}
auto nodeTotalNum = meshapi.GetNodeCount();
for (size_t i = 0; i < nodeTotalNum; i++)
{
auto node = meshapi.GetNodeByIndex(i);
}
AMCAX::Coord3d NMPoint3
Type of point/vector.
Definition: Macros.hpp:25
DimType
Type of dimension.
Definition: Macros.hpp:58
Set the face groups
Add, delete, modify, and query of the face groups.
nmapi.CreatePhysicalSet(DimType::D2, { 1, 2 }, "inlet");
nmapi.CreatePhysicalSet(DimType::D2, { 3, 4 }, "outlet");
nmapi.CreatePhysicalSet(DimType::D2, { 5 }, "symmetry");
std::vector<EntTag> entTags;
nmapi.GetEntitiesInPhysicalSet(entTags, DimType::D2, "outlet");
std::set<std::string> pNames;
nmapi.GetPhysicalSets(pNames, DimType::D2);
Output mesh files
Output mesh files in user-specified formats, such as OBJ/VTK.
meshapi.Write("flmsh.vtk", OutFileType::VTK);
meshapi.Write("flmsh.obj", OutFileType::OBJ);
Click here example01 to get the full source code of the mesh partitioning example. Everyone can download it as needed.
Appendix
The complete code for this example is listed below:
#include <fstream>
#include <nlohmann/json.hpp>
#include <set>
void GenMesh()
{
const std::string cadstr = "./data/qiuwotaojian.stp";
const std::string jsonPath = "./data/mesh_para-mesh000.json";
NMAPIModel::InitLogger();
NMAPIModel nmapi;
nmapi.ImportModel(cadstr);
nlohmann::json paraJ = nlohmann::json::parse(std::ifstream(jsonPath));
nmapi.GenerateMesh(paraJ.dump());
auto meshapi = nmapi.GetMesh();
for (
DimType dim : {DimType::D0, DimType::D1, DimType::D2, DimType::D3})
{
std::vector<NMEntity> etVec;
nmapi.GetEntities(etVec, dim);
for (auto ent : etVec)
{
auto eTag = nmapi.EntityGetTag(ent);
auto dim = nmapi.EntityGetDim(ent);
std::vector<ElemType> typeVec;
meshapi.GetEntityElementTypes(typeVec, ent);
std::vector<NMEntity> parentVec;
nmapi.GetParentAdjacentEntities(parentVec, ent);
std::vector<NMEntity> childVec;
std::vector<Orientation> ories;
nmapi.GetChildAdjacentEntities(childVec, ories, ent);
auto entElemNum = meshapi.EntityGetElementCount(ent);
for (size_t i = 0; i < entElemNum; i++)
{
auto elem = meshapi.EntityGetElementByIndex(ent, i);
}
auto entNodeNum = meshapi.EntityGetNodeCount(ent);
for (size_t i = 0; i < entNodeNum; i++)
{
auto node = meshapi.EntityGetNodeByIndex(ent, i);
}
}
}
nmapi.GetBBox(pmin, pmax);
auto elemTotalNum = meshapi.GetElementCount();
for (size_t i = 0; i < elemTotalNum; i++)
{
auto elem = meshapi.GetElementByIndex(i);
auto elemId = meshapi.ElementGetID(elem);
auto elemType = meshapi.ElementGetType(elem);
auto nodeCount = meshapi.ElementGetNodeCount(elem);
for (size_t in = 0; in < nodeCount; in++)
{
auto node = meshapi.ElementGetNode(elem, in);
auto nodeId = meshapi.NodeGetID(node);
auto nodeEnt = meshapi.NodeGetEntity(node);
auto nodePos = meshapi.NodeGetPosition(node);
if (nmapi.EntityGetDim(nodeEnt) == DimType::D1 ||
nmapi.EntityGetDim(nodeEnt) == DimType::D2)
double u = meshapi.NodeGetFirstParameter(node);
if (nmapi.EntityGetDim(nodeEnt) == DimType::D2)
double v = meshapi.NodeGetSecondParameter(node);
}
}
auto nodeTotalNum = meshapi.GetNodeCount();
for (size_t i = 0; i < nodeTotalNum; i++)
{
auto node = meshapi.GetNodeByIndex(i);
}
nmapi.CreatePhysicalSet(DimType::D2, { 1, 2 }, "inlet");
nmapi.CreatePhysicalSet(DimType::D2, { 3, 4 }, "outlet");
nmapi.CreatePhysicalSet(DimType::D2, { 5 }, "symmetry");
std::vector<EntTag> entTags;
nmapi.GetEntitiesInPhysicalSet(entTags, DimType::D2, "outlet");
std::set<std::string> pNames;
nmapi.GetPhysicalSets(pNames, DimType::D2);
meshapi.Write("flmsh.vtk", OutFileType::VTK);
meshapi.Write("flmsh.obj", OutFileType::OBJ);
}